Fast Numerical Optimization for Genome Sequencing Data in Population Biobanks
Published in Bioinformatics, 2021
In this paper led by Ruilin Li, we describe memory-efficient and multi-threaded parallelized implementations of snpnet (snpnet-2.0 and sparse-snpnet).
In snpnet-2.0, we apply the iteratively reweighted least squares (IRLS) algorithm and demonstrate substantial speed-up while maintaining competitive predictive performance compared to the original snpnet, as well as other commonly used tools, including bigstatsr, BOLT-LMM, and LDpred2.
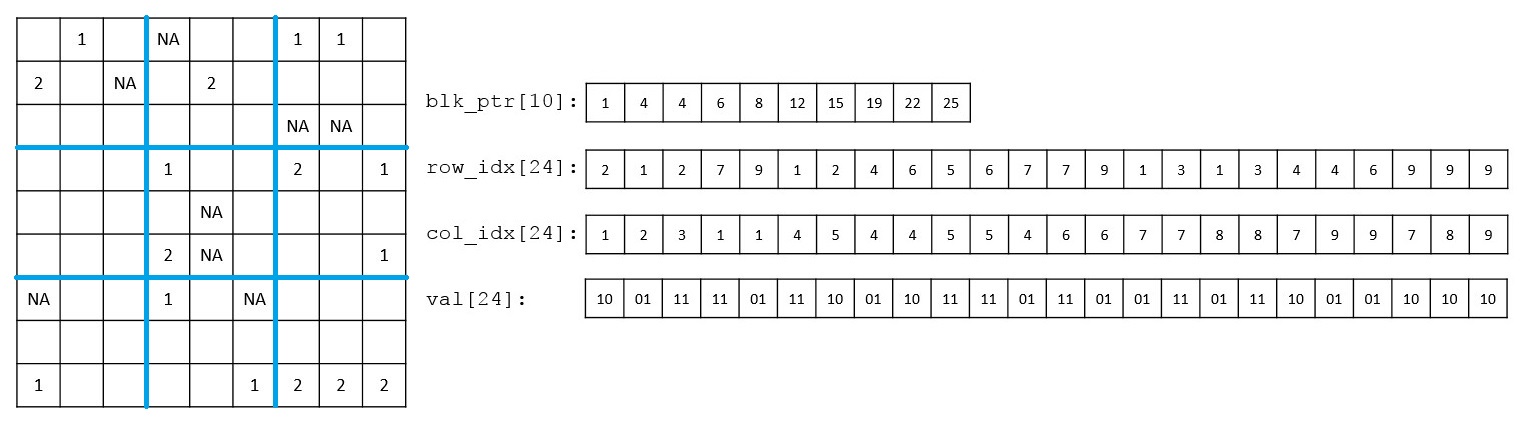
In sparse-snpnet, we leverage the extreme sparsity in whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing datasets, represent genetic data using a compressed sparse block (CSB) format, and apply proximal gradient descent, eliminating the need for variable screening while optimizing computational efficiency.
Overall, the paper presents substantial advancements over previous works in polygenic risk modeling, particularly beyond the Batch Iterative Screening Lasso (BASIL) approach used in earlier snpnet implementations.
- BASIL algorithm and
snpnetfor quantitative and binary traits, J. Qian et al, 2020 - Single-response Cox model, Li et al, 2020
Reference: R. Li, C. Chang, Y. Tanigawa, B. Narasimhan, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, Fast Numerical Optimization for Genome Sequencing Data in Population Biobanks. Bioinformatics 37(22), 4148-4155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab452 (full text)
