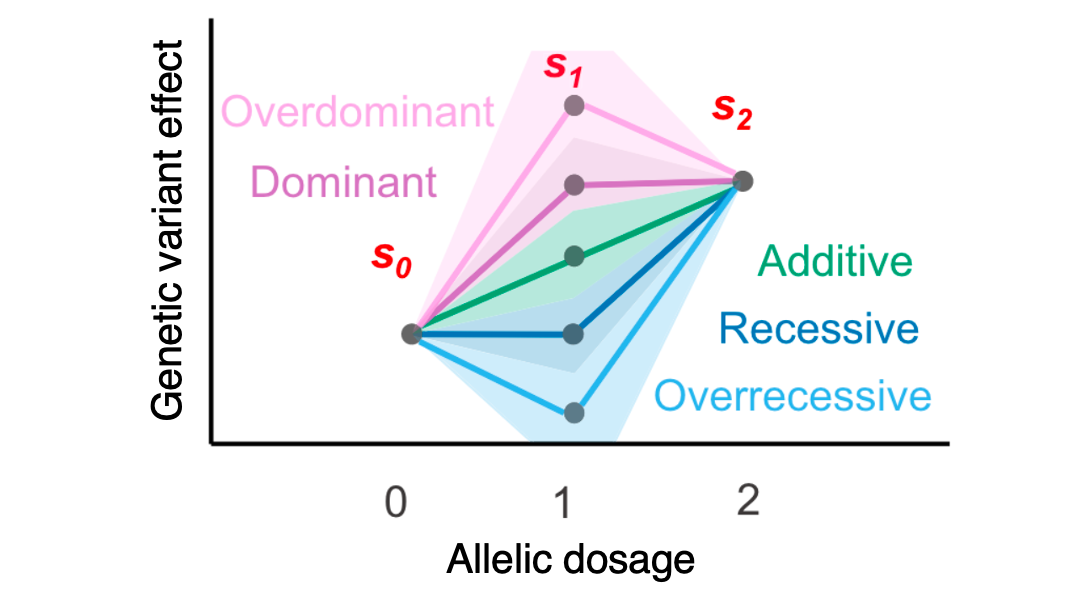
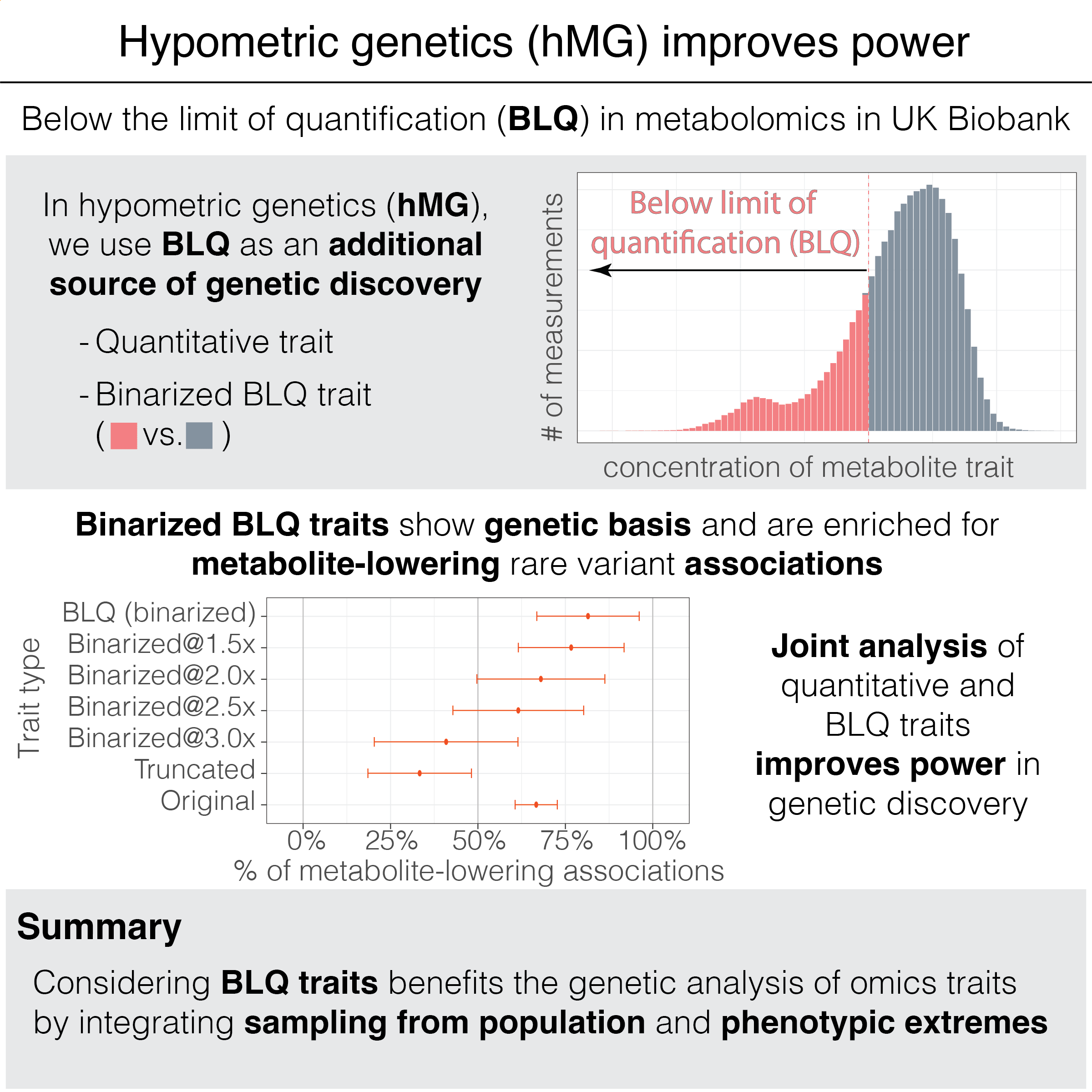
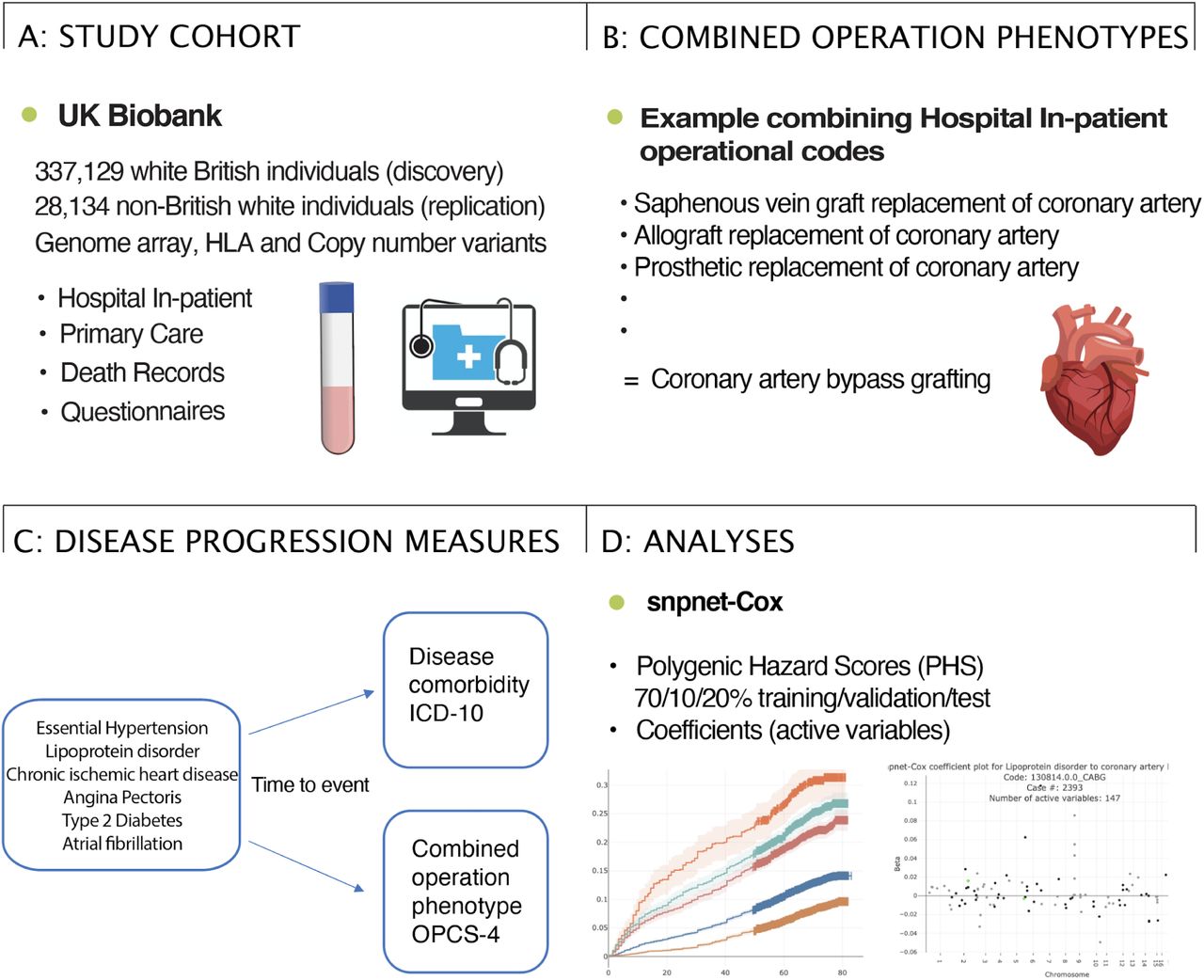
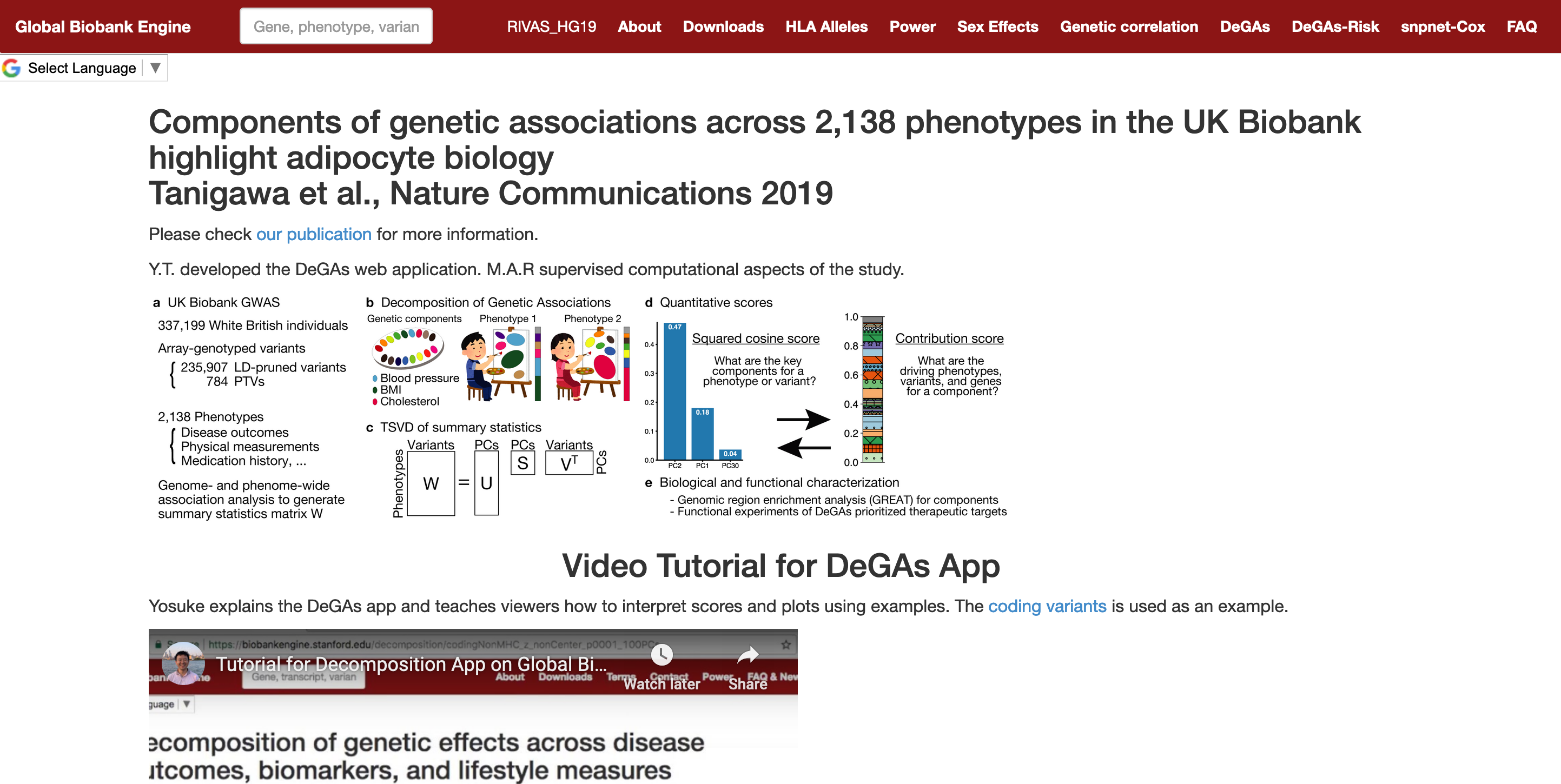
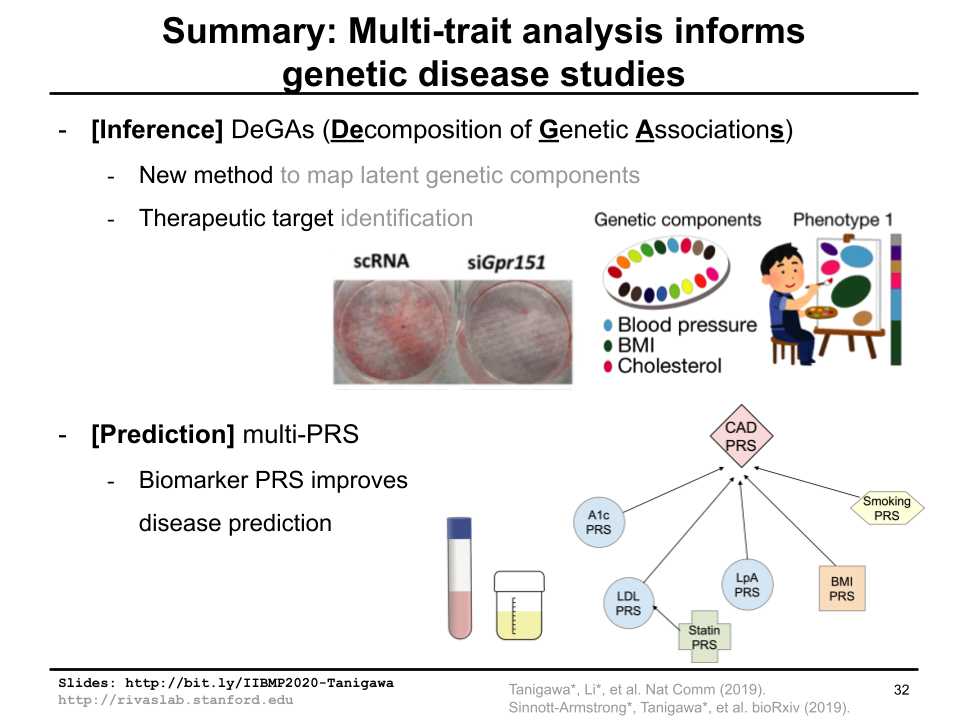
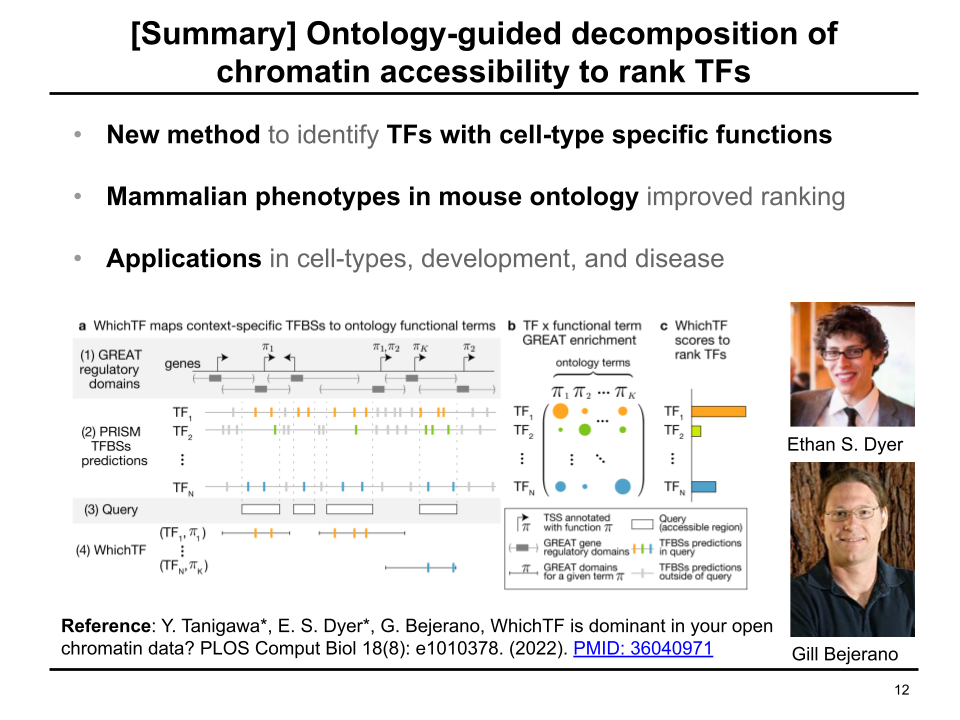
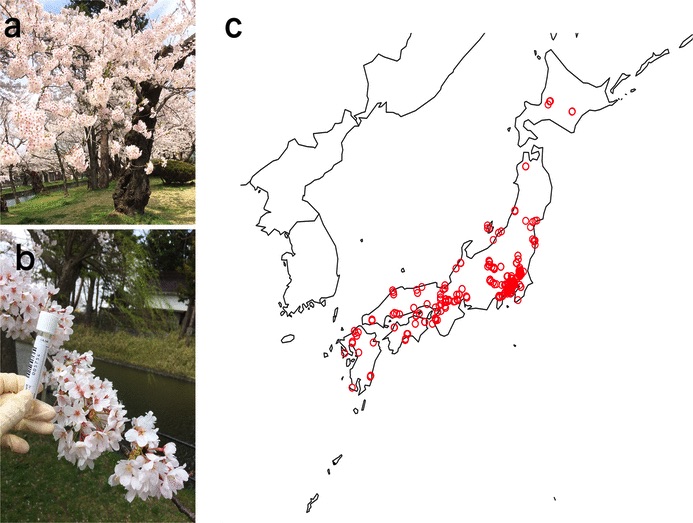
Collaborative environmental DNA sampling from petal surfaces of flowering cherry Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ across the Japanese archipelago
Published in Journal of Plant Research, 2018
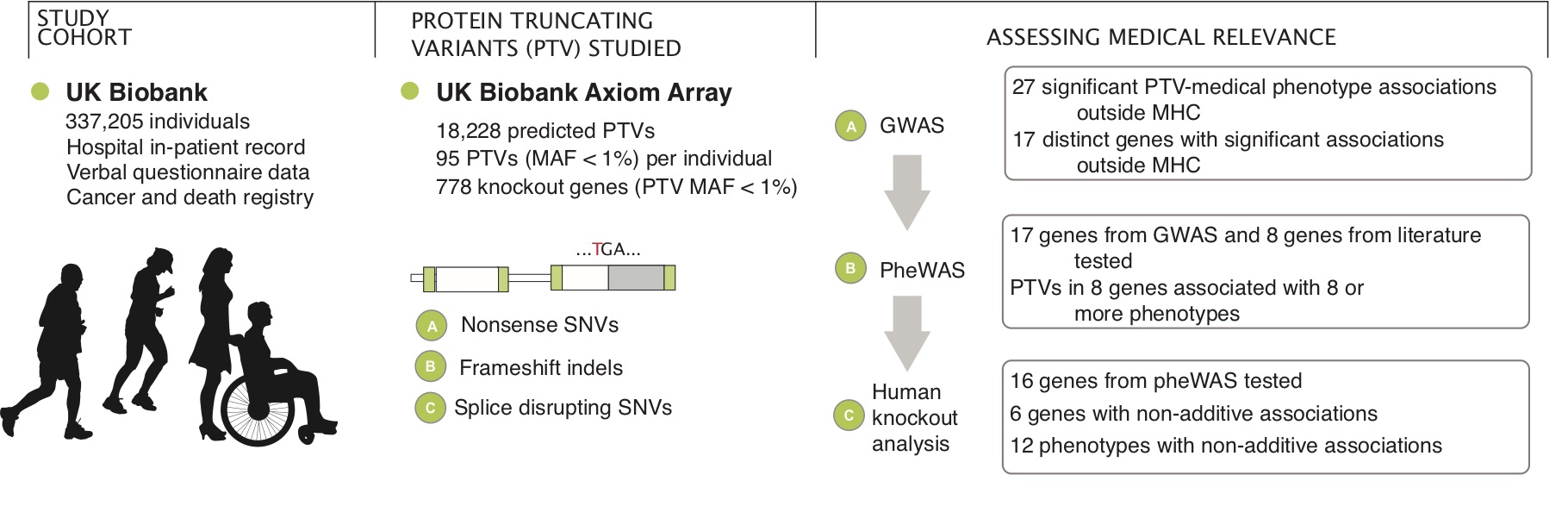
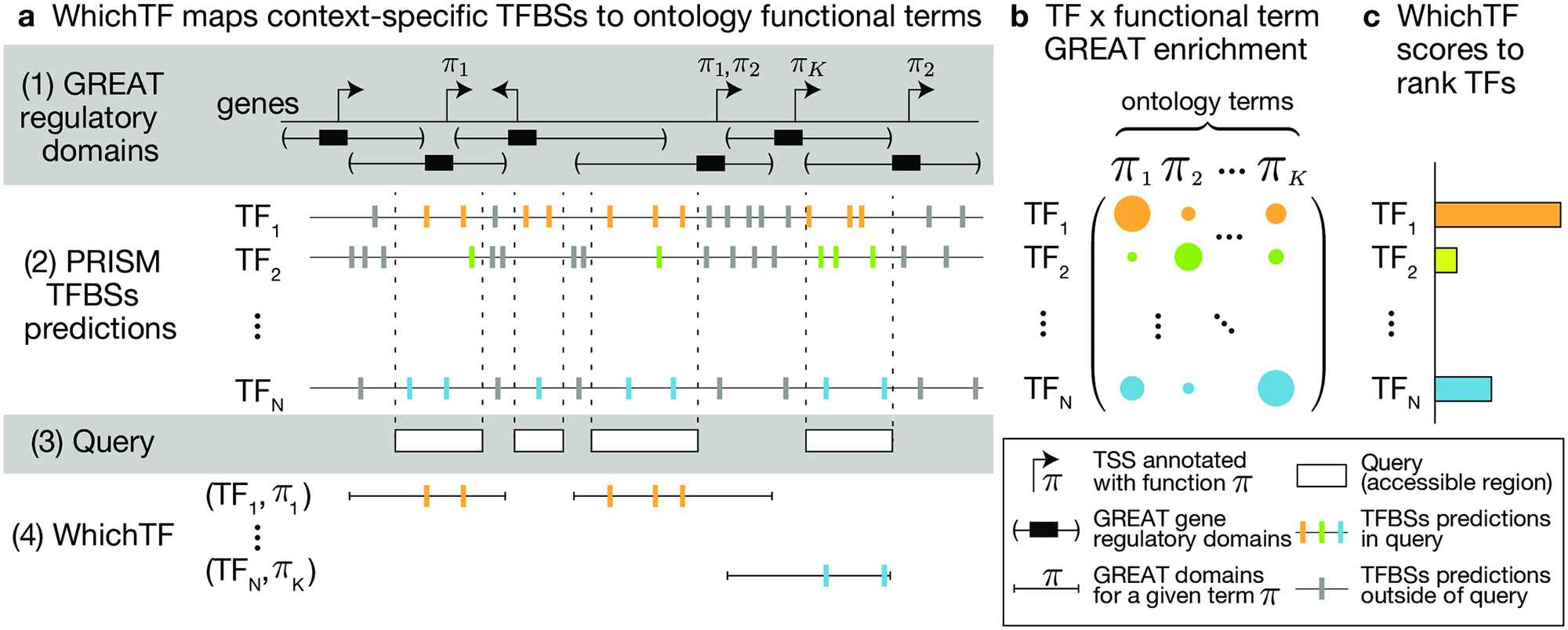
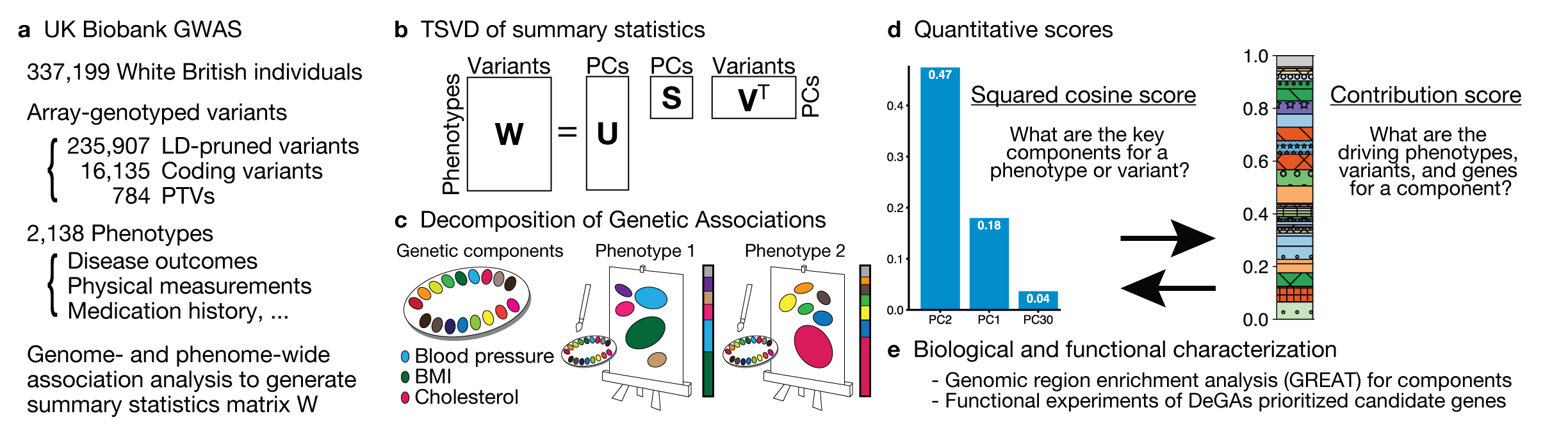
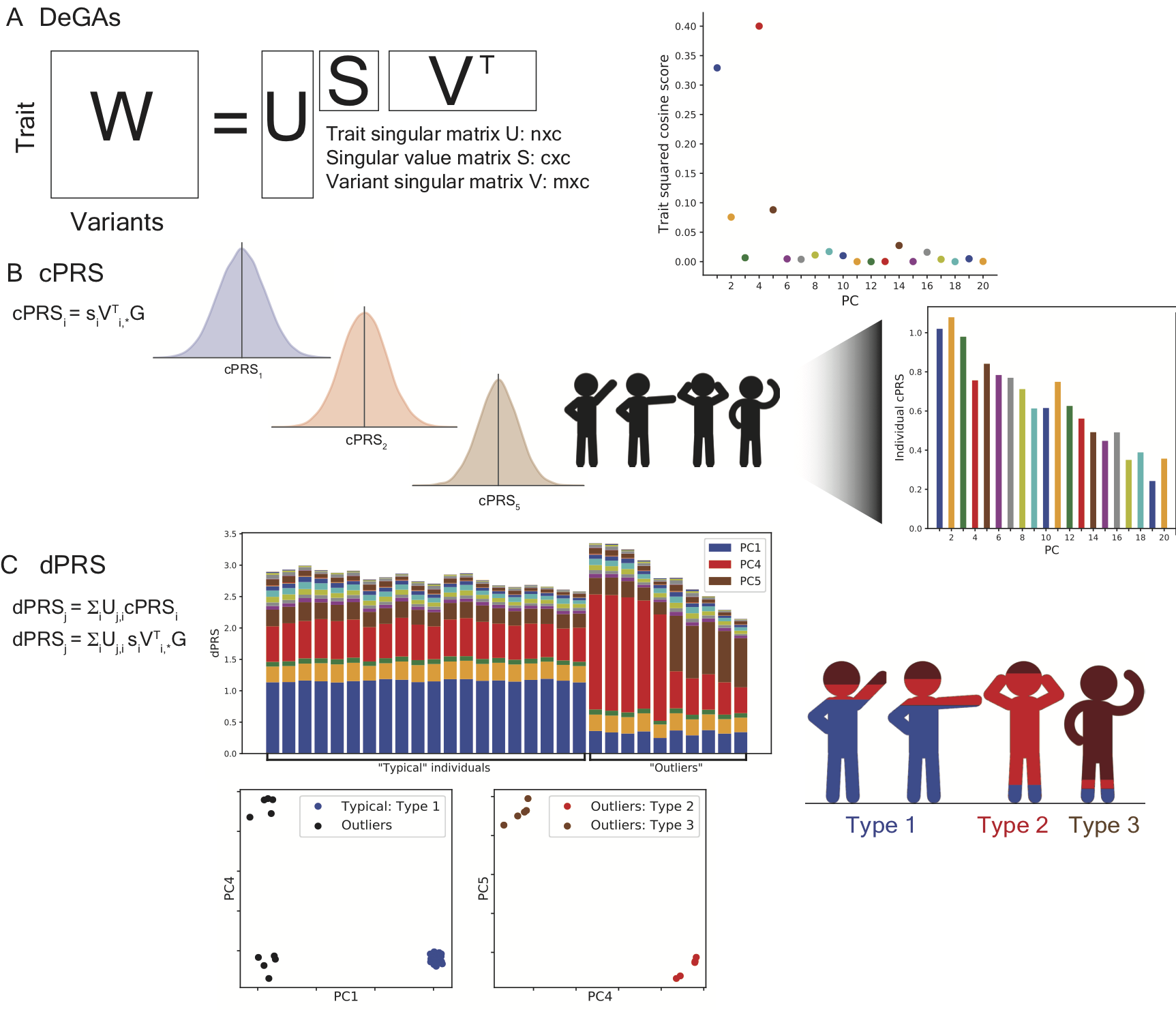
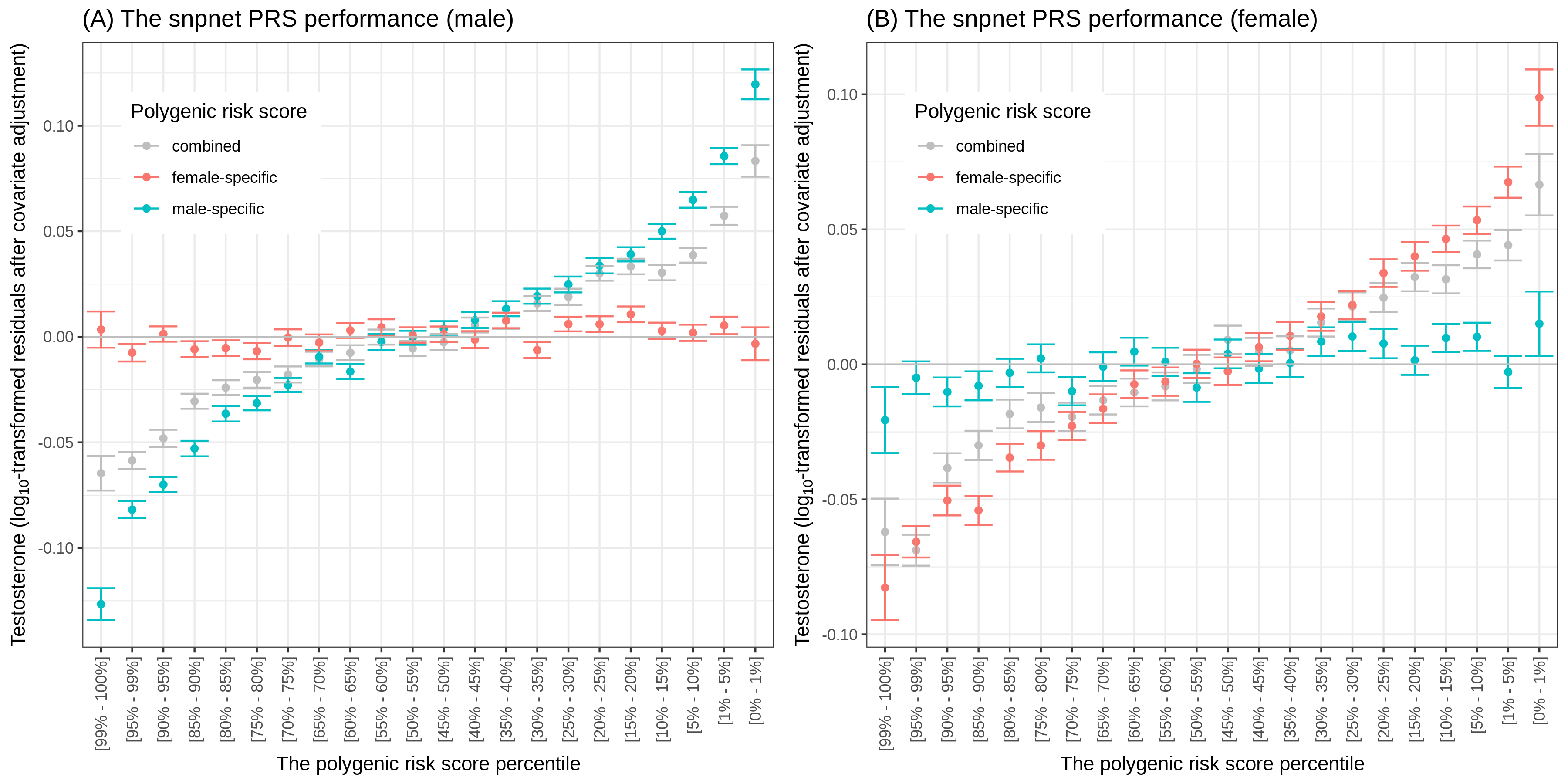
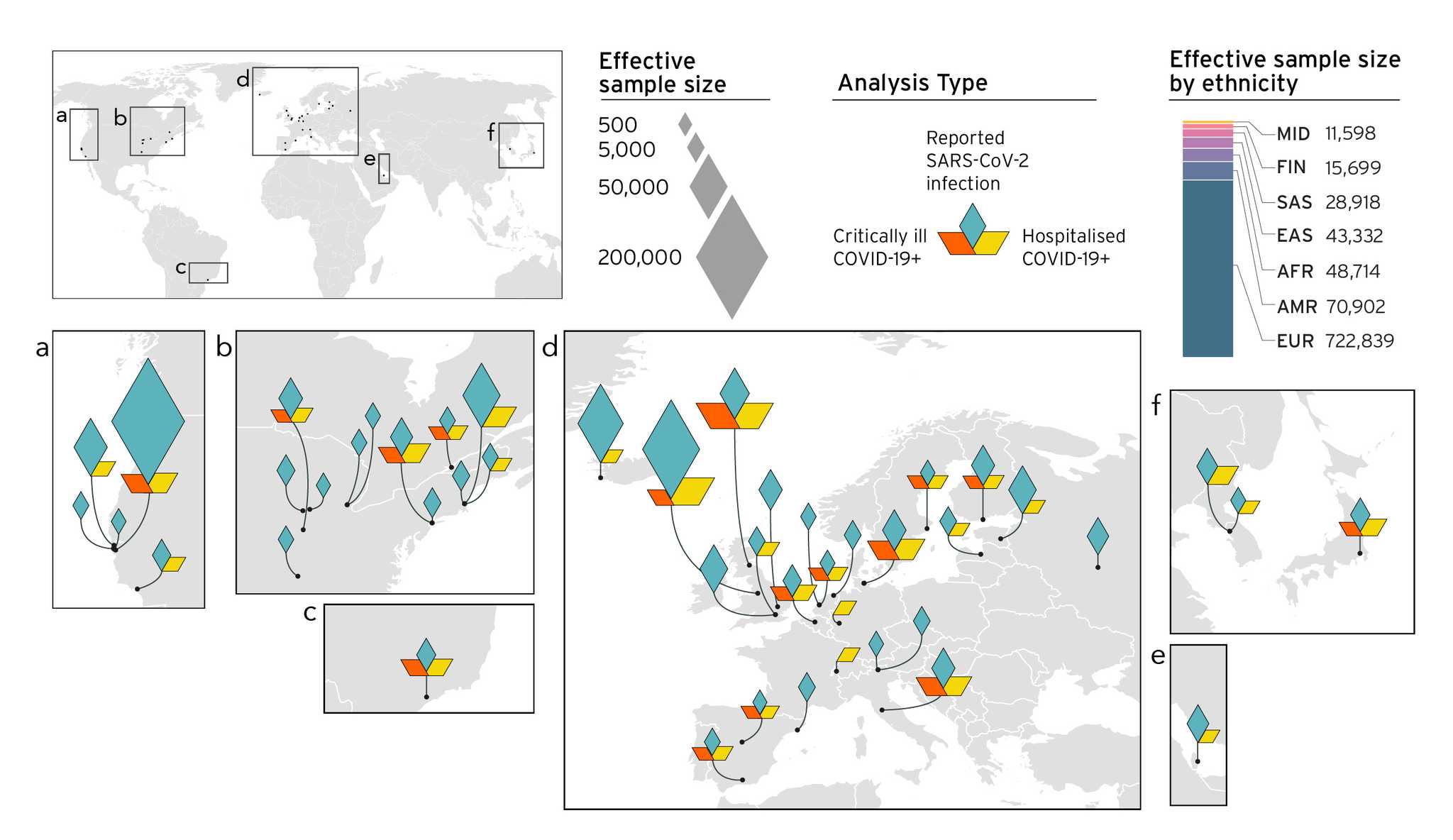
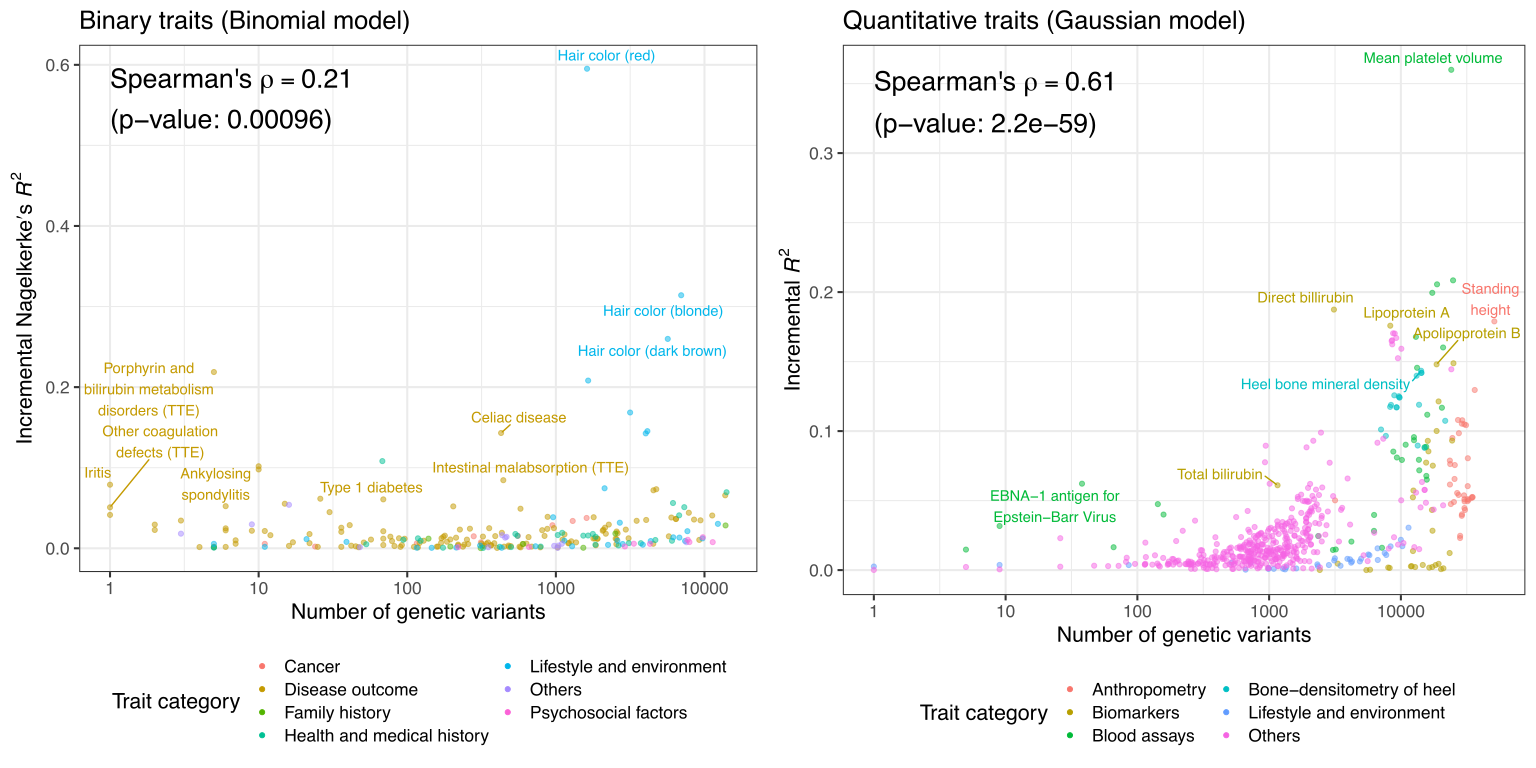
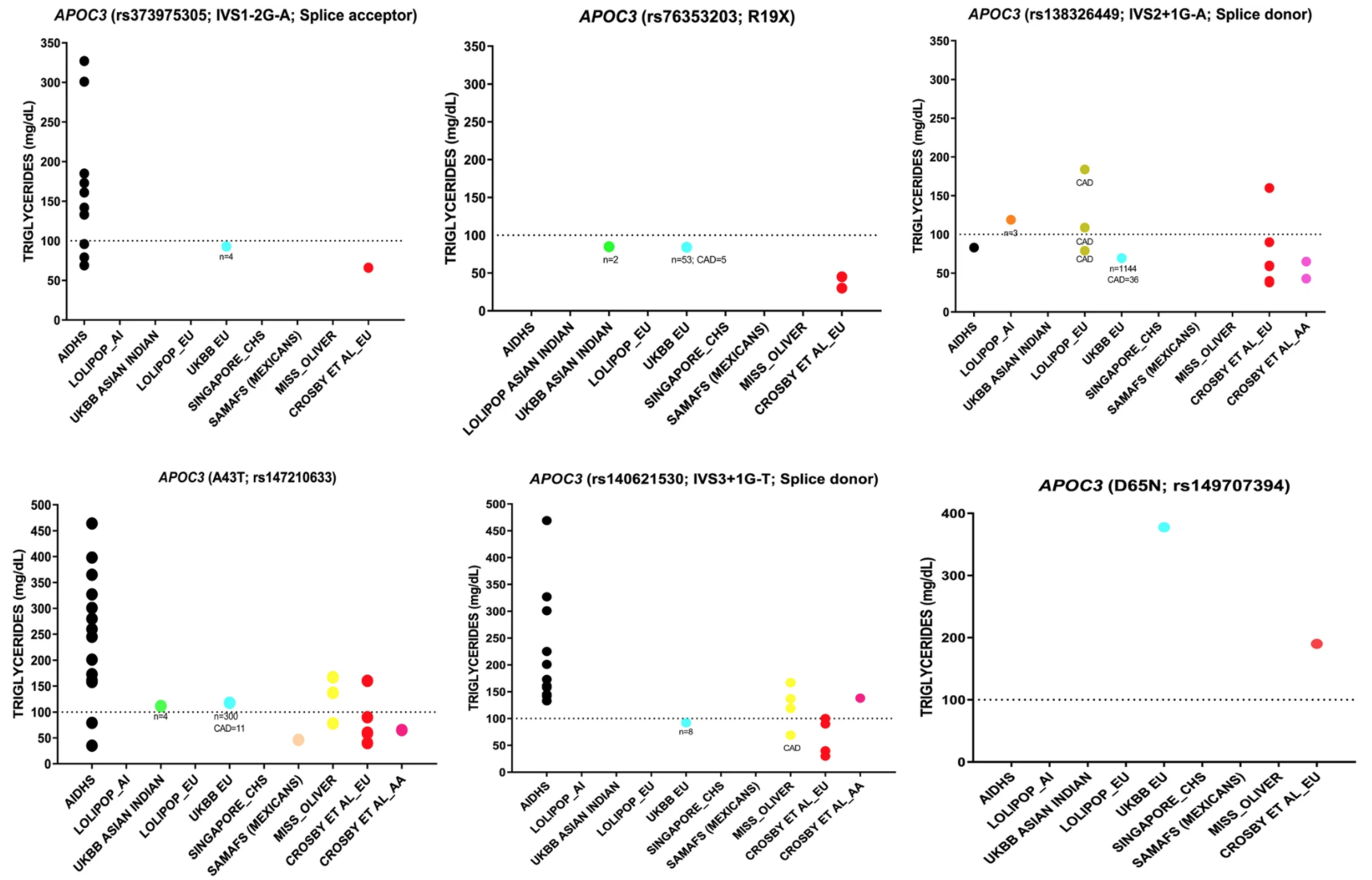
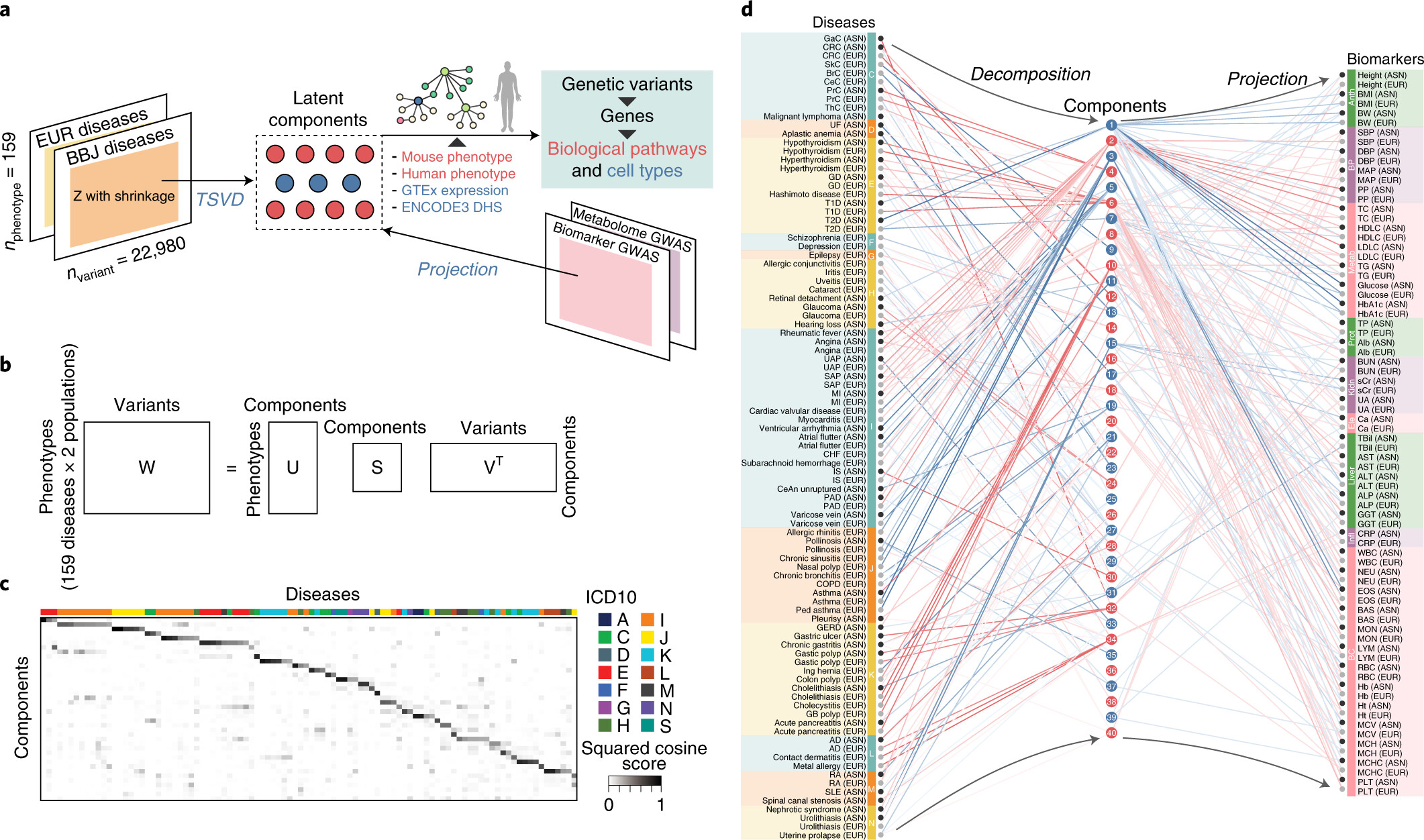
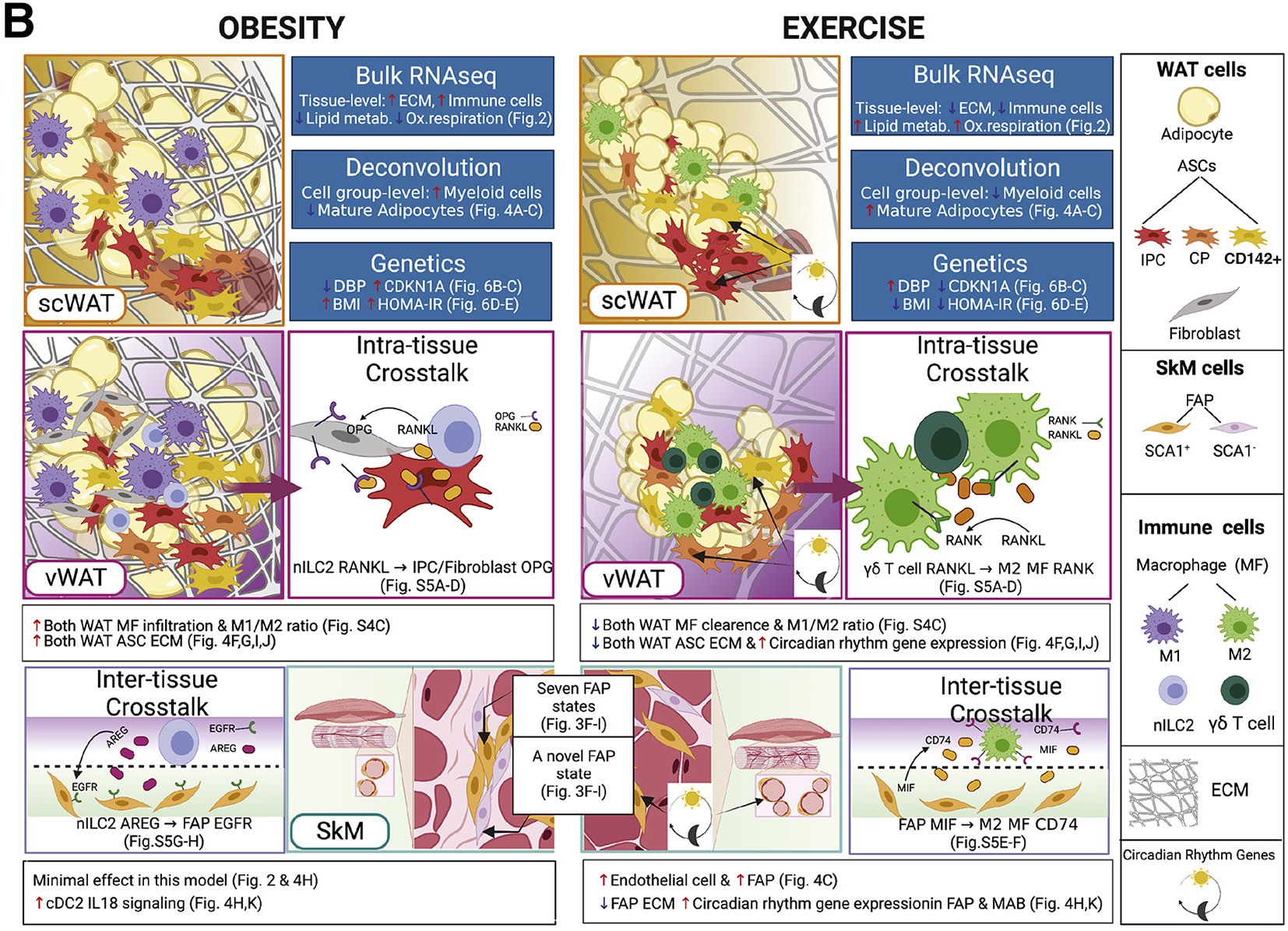
Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ is Japan’s most commonly cultivated cherry blossoms tree. Thanks to widespread grafting, it blooms synchronously in the same climate condition, which is suitable for the subject of ‘Ohanami,’ flower viewing parties in Japan. Despite the host genetics’ homogeneity, the composition of environmental DNA (eDNA) on the petal surface was unclear. As a pilot project, we performed community-based eDNA profiling across 577 eDNA samples and 149 collaborators. A preliminary analysis identified the DNA of common plant species, including the one that likely originated from the pollen of the Japanese cedar. Our results highlight the value of crowdsourced eDNA sampling and analyses in ecological studies.
Reference: T. Ohta, T. Kawashima, N. O. Shinozaki, A. Dobashi, S. Hiraoka, T. Hoshino, K. Kanno, T. Kataoka, S. Kawashima, M. Matsui, W. Nemoto, S. Nishijima, N. Suganuma, H. Suzuki, Y. Taguchi, Y. Takenaka, Y. Tanigawa, M. Tsuneyoshi, K. Yoshitake, Y. Sato, R. Yamashita, K. Arakawa, W. Iwasaki, Collaborative environmental DNA sampling from petal surfaces of flowering cherry Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ across the Japanese archipelago. J Plant Res. 131, 709-717 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-018-1017-x