Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
About me
日本語のプロフィール
The pdf file of my CV is shown.
The list of publications is shown in the page. Please also check my Google Scholar profile for the latest information.
Published:
We are looking for motivated students and postdocs to join the lab. Please find me for coffee chat.
Published:
I am excited to announce that I have joined UCLA as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Bioengineering.
Published:
Yosuke was in the academic job market in the 2024/25 cycle. I am grateful for the support I received during the critical time of transition.
Published:
Adobe Illustrator and similar vector graphics software allows you to prepare figures for scientific publication. As a computational researcher working on statistical methods, you may want to use LaTeX equations in figures.
Published:
Here are the exciting moments in 2024! We have other news posts.
Published:
Here are the exciting moments in 2023! We have other news posts.
Published:
This page has a long list of resources to learn about efficient large-scale computing.
Published:
私は,生物情報科学という,生物学と情報科学の融合分野について,学部生の段階で先進的な教育を受ける機会に恵まれました。私が在籍したときは,学年の学生人数は10人程度,一方で教授陣も約10人ほどと,学生定数:教員数がほぼ 1:1 というとても恵まれた環境で,最先端の学問分野を指導していただくことができました。
Published:
Here are the exciting moments in 2022! We have other news posts.
Published:
This post is written in Japanese. Yosuke explains his life at Stanford.
Published:
Here are the exciting moments in 2021! We have other news posts.
Published:
There are several column-oriented data formats. To store and query large table files, we explor those modern technologies. Here, I have some snippets.
Published:
Occasionally, Yosuke performs science outreach talks. This post explains an example of such activities targeted for Japanese high schoolers.
Published:
Kinesis Advantageous 2 keyboard.
Published:
Terminal multiplexer software, such as tmux and screen, is a useful tool. When using tmux on mac, I encountered the following error.
Published:
PLINK is a well-established software for genetic analysis. In many projects, we use plink2 for genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and other genetic analyses using the raw genotype matrix.
Published:
When you’re working on extremely small floating numbers in R (such as when you have strong p-values), there are a few options.
Published:
This post is written in Japanese. Yosuke explains his fellowship support from the Funai Foundation for Information Technology, which supports Japanese citizens and permanent residents. You may have some luck with DeepL translator.
Published:
Ruby bundler is a convenient tool to manage the Ruby environments. This website, for example, is built with Jekyll.
Published:
Figshare is a data hosting service to make the scientific results available. While they have a nice web interface to upload your files, you sometimes want to upload a large file (> 5GB, for example). For that purpose, they provide an API access. Here is my example on how to use their API.
Published:
Here, I list publicly available resources.
Published:
SLURM is one of the most common job scheduler used in many high performance cluster computing severs (HPC). Here, I summarize useful SLURM commands.
Published:
This post is written in Japanese. Please check my post on our recent preprint, Tanigawa, Y. & Rivas, M. Initial Review and Analysis of COVID-19 Host Genetics and Associated Phenotypes. (2020). Also, you may have some luck with DeepL translator.
Published:
Thanks to my colleagues and supports from the community, we had several exciting moments in 2020! We have other news posts.
Published in Journal of Plant Research, 2018
Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ is Japan’s most commonly cultivated cherry blossoms tree. Thanks to widespread grafting, it blooms synchronously in the same climate condition, which is suitable for the subject of ‘Ohanami,’ flower viewing parties in Japan. Despite the host genetics’ homogeneity, the composition of environmental DNA (eDNA) on the petal surface was unclear. As a pilot project, we performed community-based eDNA profiling across 577 eDNA samples and 149 collaborators. A preliminary analysis identified the DNA of common plant species, including the one that likely originated from the pollen of the Japanese cedar. Our results highlight the value of crowdsourced eDNA sampling and analyses in ecological studies.
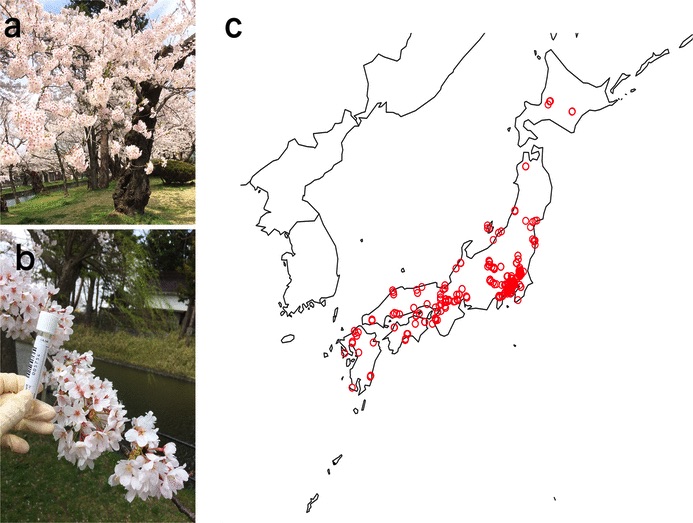
Reference: T. Ohta, T. Kawashima, N. O. Shinozaki, A. Dobashi, S. Hiraoka, T. Hoshino, K. Kanno, T. Kataoka, S. Kawashima, M. Matsui, W. Nemoto, S. Nishijima, N. Suganuma, H. Suzuki, Y. Taguchi, Y. Takenaka, Y. Tanigawa, M. Tsuneyoshi, K. Yoshitake, Y. Sato, R. Yamashita, K. Arakawa, W. Iwasaki, Collaborative environmental DNA sampling from petal surfaces of flowering cherry Cerasus × yedoensis ‘Somei-yoshino’ across the Japanese archipelago. J Plant Res. 131, 709-717 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-018-1017-x
Published in Nature Communications, 2018
Using the UK Biobank population cohort, we investigated the genetic effects of Protein-truncating variants (PTVs) and the clinical impacts.
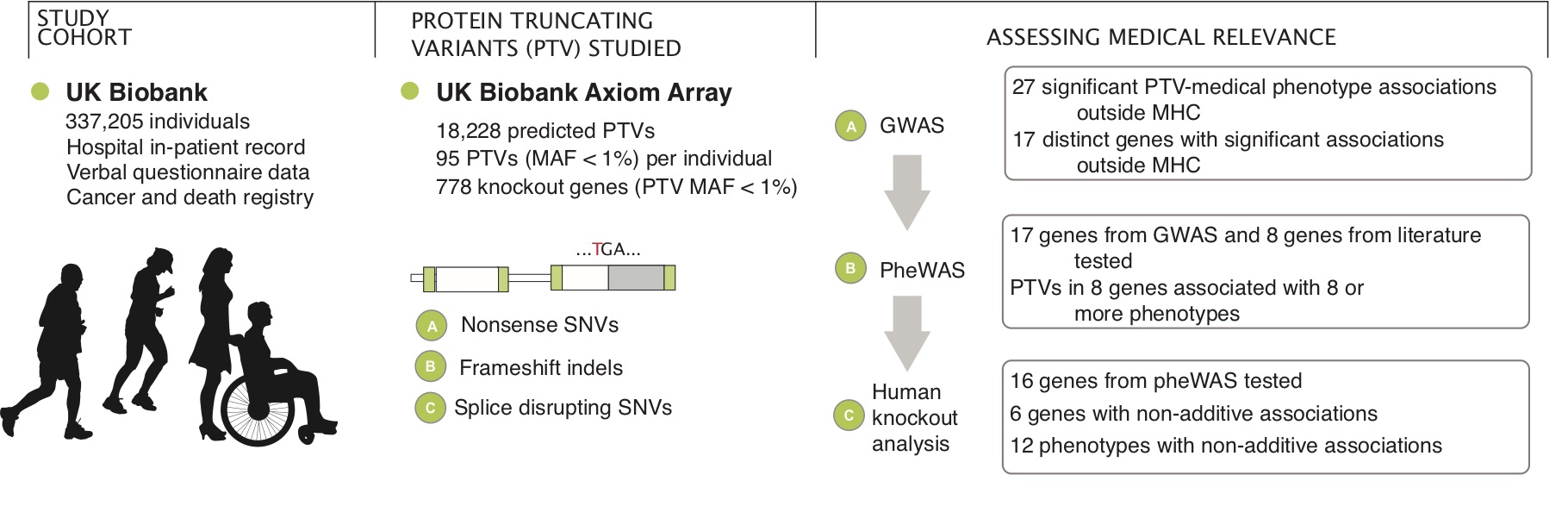
Reference: C. DeBoever, Y. Tanigawa, M. E. Lindholm, G. McInnes, A. Lavertu, E. Ingelsson, C. Chang, E. A. Ashley, C. D. Bustamante, M. J. Daly, M. A. Rivas, Medical relevance of protein-truncating variants across 337,205 individuals in the UK Biobank study. Nat Commun. 9, 1612 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03910-9
Published in Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, 2018
We propose SNPs2ChIP, a method to infer biological functions of non-coding variants through unsupervised statistical learning methods applied to publicly-available epigenetic datasets.
Reference: S. Anand, L. Kalesinskas, C. Smail, Y. Tanigawa, SNPs2ChIP: Latent Factors of ChIP-seq to infer functions of non-coding SNPs. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2019, 24: 184-195 (WORLD SCIENTIFIC, 2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/9789813279827_0017
Published in Bioinformatics, 2018
We present Global Biobank Engine as a platform to visualize genome- and phenome-wide associations and perform statistical inference using those association data.
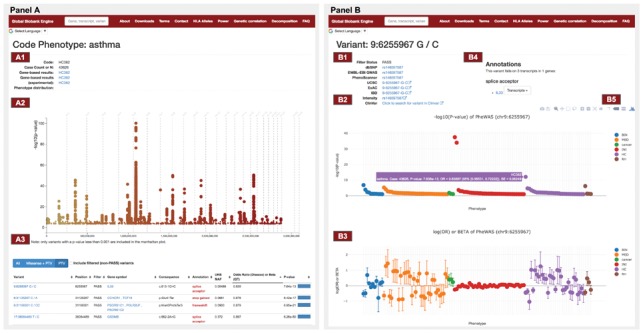
Reference: G. McInnes, Y. Tanigawa, C. DeBoever, A. Lavertu, J. E. Olivieri, M. Aguirre, M. A. Rivas, Global Biobank Engine: enabling genotype-phenotype browsing for biobank summary statistics. Bioinformatics 35(14), 2495-2497 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty999
Published in Molecular Psychiatry, 2019
Using two independent datasets from genotyped cohorts (UK Biobank and electronic medical record (EMR) in Vanderbilt University Medical Center), we quantified the heritability estimates of suicide attempts. We also showed the shared genetic basis of suicide attempts and other phenotypes.
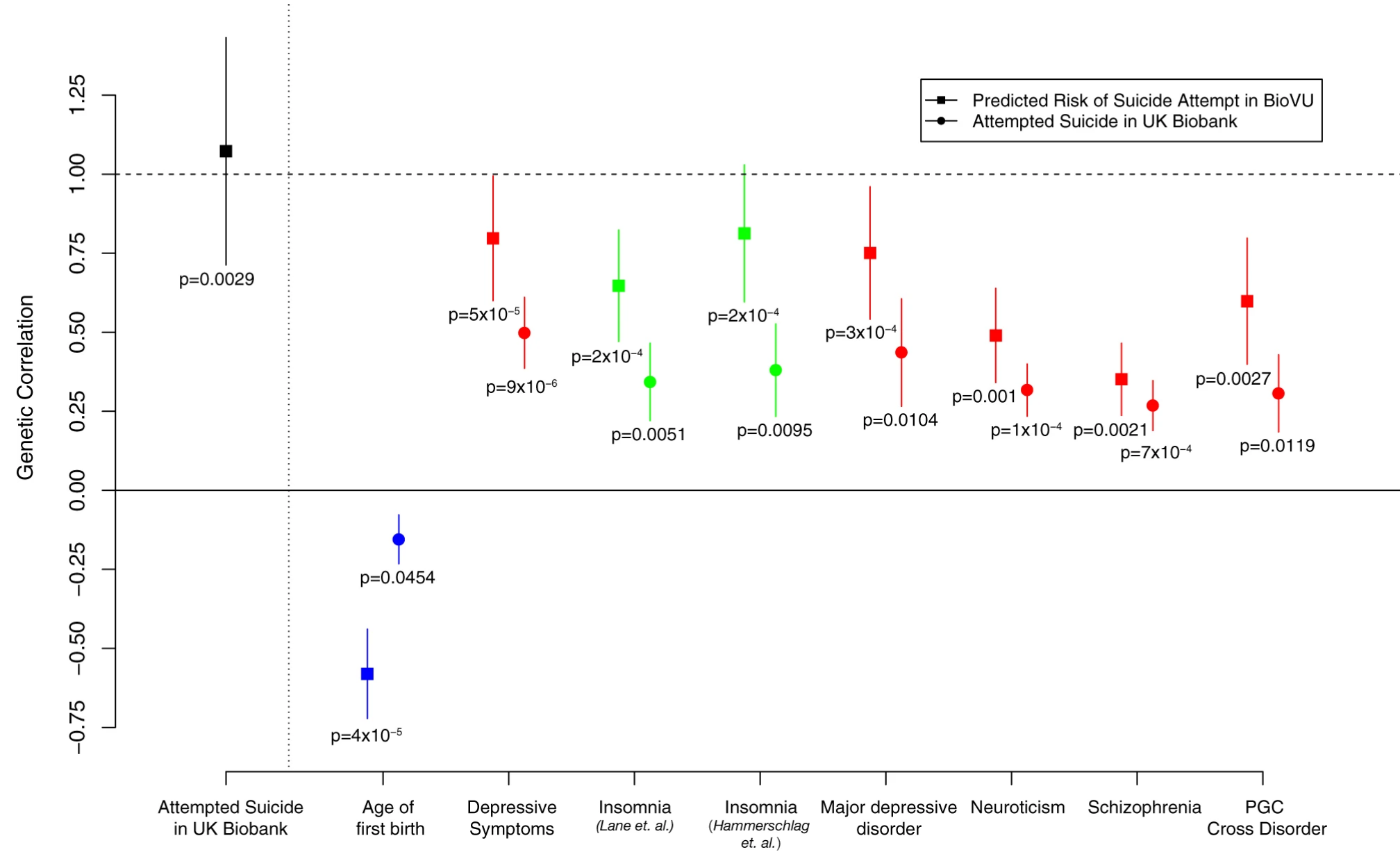
Reference: D. M. Ruderfer, C. G. Walsh, M. W. Aguirre, Y. Tanigawa, J. D. Ribeiro, J. C. Franklin, M. A. Rivas, Significant shared heritability underlies suicide attempt and clinically predicted probability of attempting suicide. Mol Psychiatry. 25(10), 2422-2430 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0326-8
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
In this project led by Junyang Qian, we developed BASIL, a novel algorithm to fit large-scale L1 penalized (Lasso) regression model using an iterative procedure, and implemented R snpnet package specially designed for genetic data. We demonstrate the ability of this approach in an application to UK Biobank dataset.

Reference: J. Qian, Y. Tanigawa, W. Du, M. Aguirre, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, T. Hastie, A Fast and Scalable Framework for Large-scale and Ultrahigh-dimensional Sparse Regression with Application to the UK Biobank. bioRxiv, 630079 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/630079
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
We characterized the genetics of 35 biomarkers in UK Biobank. We performed the association and fine-mapping analysis to prioritize the causal variants, constructed the polygenic risk score (PRS) models, and evaluated their medical relevance with causal inference and PRS-PheWAS. We demonstrate a new approach, called multi-PRS, to improve PRS by combining PRSs across traits.
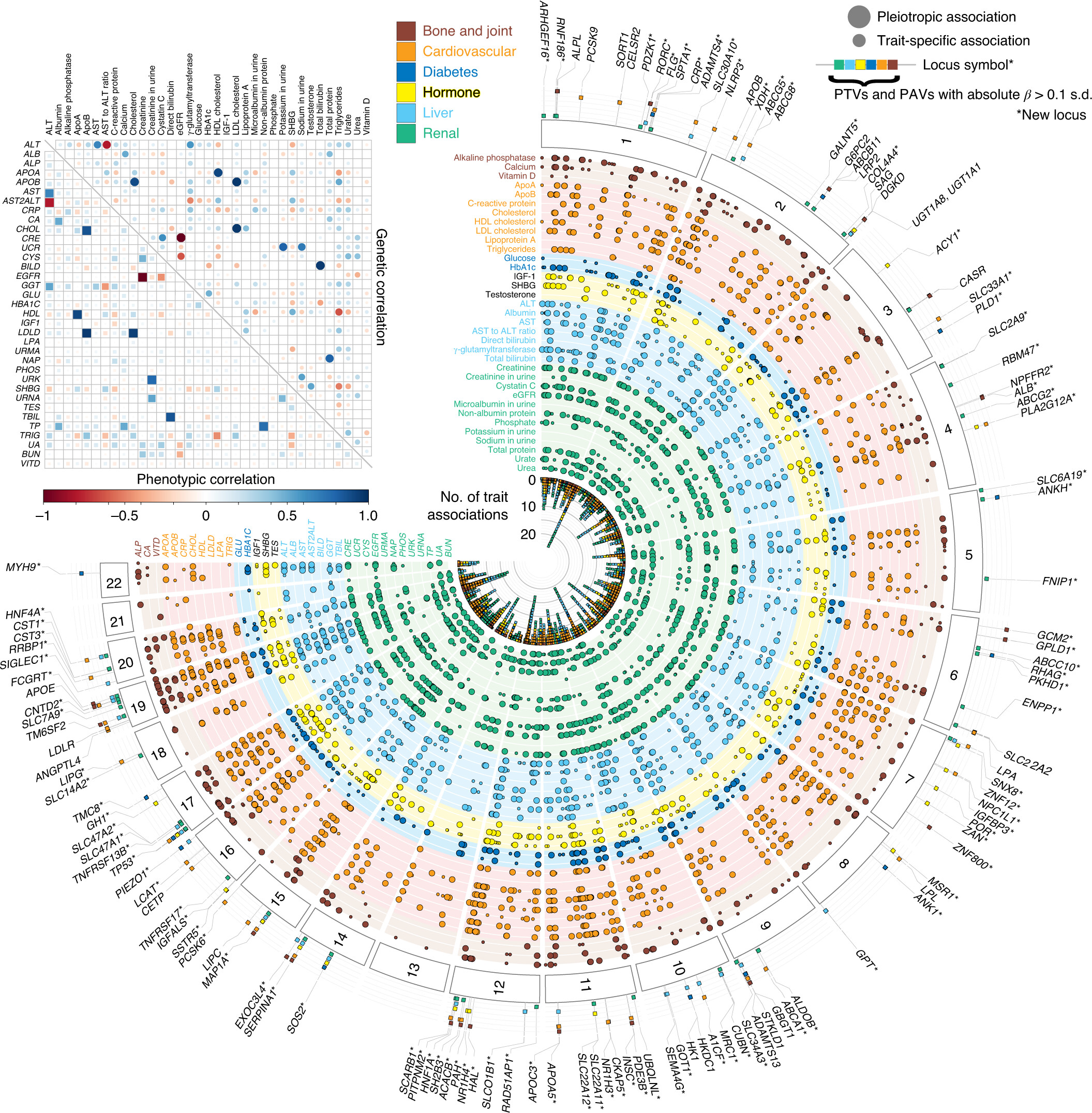
Reference: N. Sinnott-Armstrong*, Y. Tanigawa*, D. Amar, N. J. Mars, M. Aguirre, G. R. Venkataraman, M. Wainberg, H. M. Ollila, J. P. Pirruccello, J. Qian, A. Shcherbina, FinnGen, F. Rodriguez, T. L. Assimes, V. Agarwala, R. Tibshirani, T. Hastie, S. Ripatti, J. K. Pritchard, M. J. Daly, M. A. Rivas, Genetics of 38 blood and urine biomarkers in the UK Biobank. bioRxiv, 660506 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/660506
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, M. Wainberg, J. Karjalainen, T. Kiiskinen, S. Lemmelä, J. A. Turunen, A. Palotie, FinnGen, M. J. Daly, M. A. Rivas, Rare protein-altering variants in ANGPTL7 lower intraocular pressure and protect against glaucoma. bioRxiv, 677443 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/677443
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
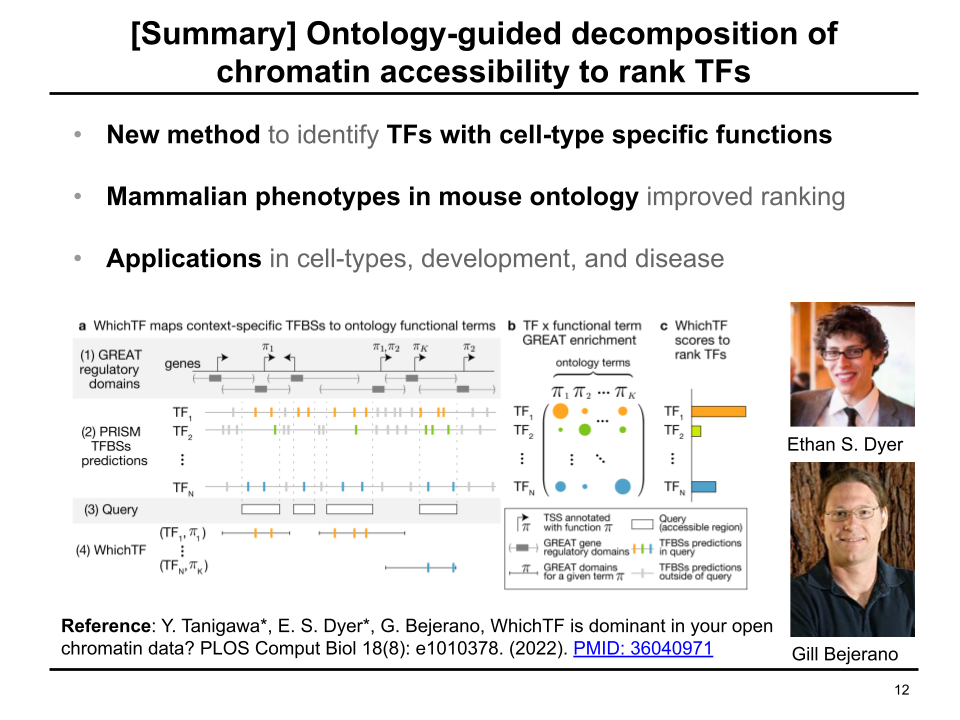
To identify functionally important transcription factors (TFs), we developed WhichTF. This method takes experimentally characterized chromatin accessibilty measure as the input and returns a ranked list of TFs. We combined available genomic resources, such as gene regulatory domain models, conservation-aware prediction of TF binding sites, and ontology annotation of genes, for this task.
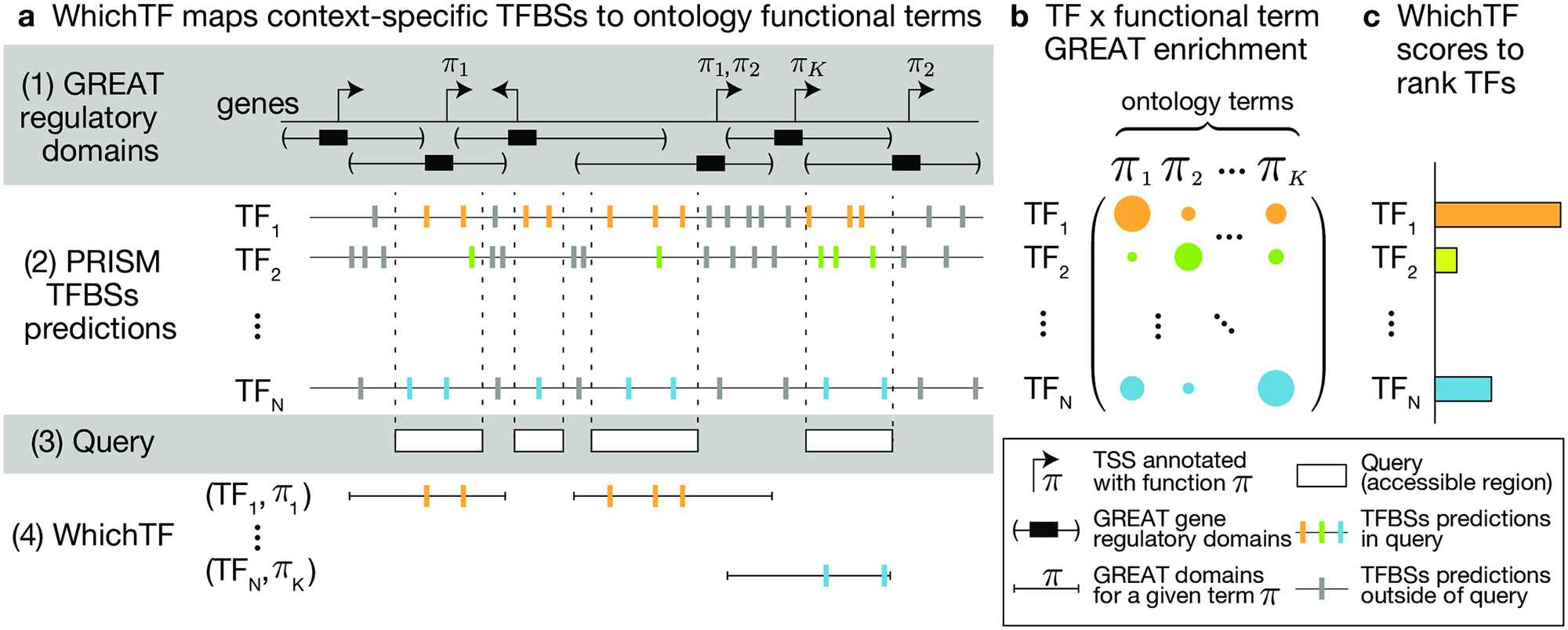
Reference: Y. Tanigawa*, E. S. Dyer*, G. Bejerano, WhichTF is dominant in your open chromatin data? bioRxiv, 730200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/730200
Published in Nature Communications, 2019
While many pleiotropic genetic loci have been identified, how they contribute to phenotypes across traits and diseases is unclear. Here, the authors propose a decomposition of genetic associations (DeGAs), which uses singular value decomposition to characterize the underlying latent structure of genetic associations of 2,138 phenotypes.
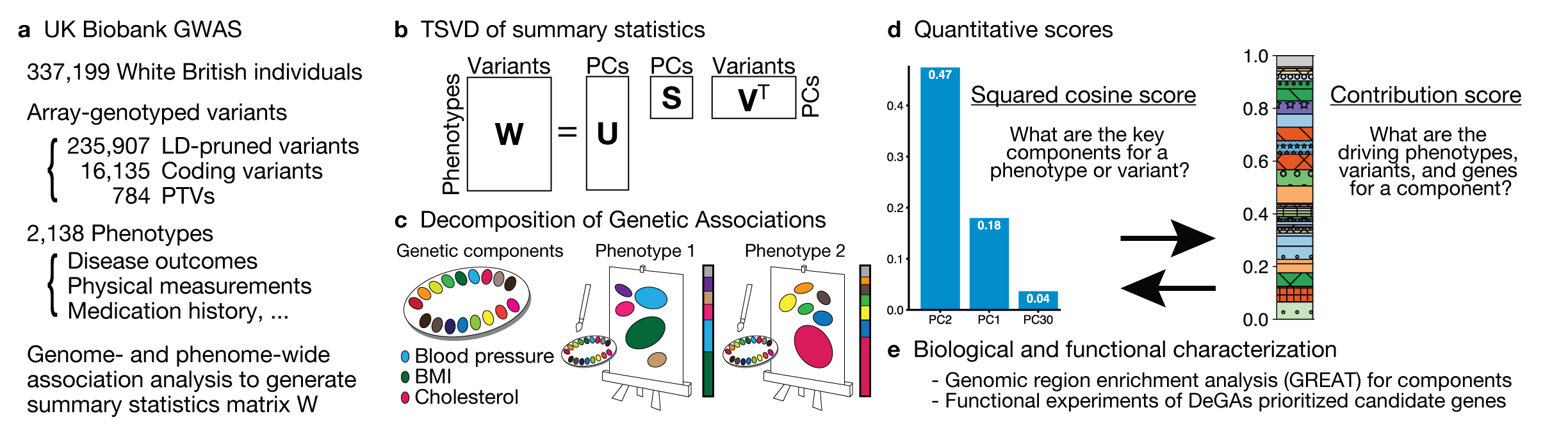
Reference: Y. Tanigawa*, J. Li*, J. M. Justesen, H. Horn, M. Aguirre, C. DeBoever, C. Chang, B. Narasimhan, K. Lage, T. Hastie, C. Y. Park, G. Bejerano, E. Ingelsson, M. A. Rivas, Components of genetic associations across 2,138 phenotypes in the UK Biobank highlight adipocyte biology. Nat Commun. 10, 4064 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11953-9
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, M. A. Rivas, Reported CCR5-∆32 deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is explained by poor genotyping of rs62625034. bioRxiv, 791517 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/791517
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
Polygenic risk score (PRS) has been proposed for disease risk prediction with potential clinical relevance for some traits, but its personalized interpretation is generally difficult, especially when there exist disease subtypes driven by different genetic components. Here, we introduce dPRS (DeGAs-PRS) as an extension of Decomposition of Genetic Associations (DeGAs) to decompose the polygenic risk of individuals into latent components of genetic associations characterized from hundreds of thousands of traits.
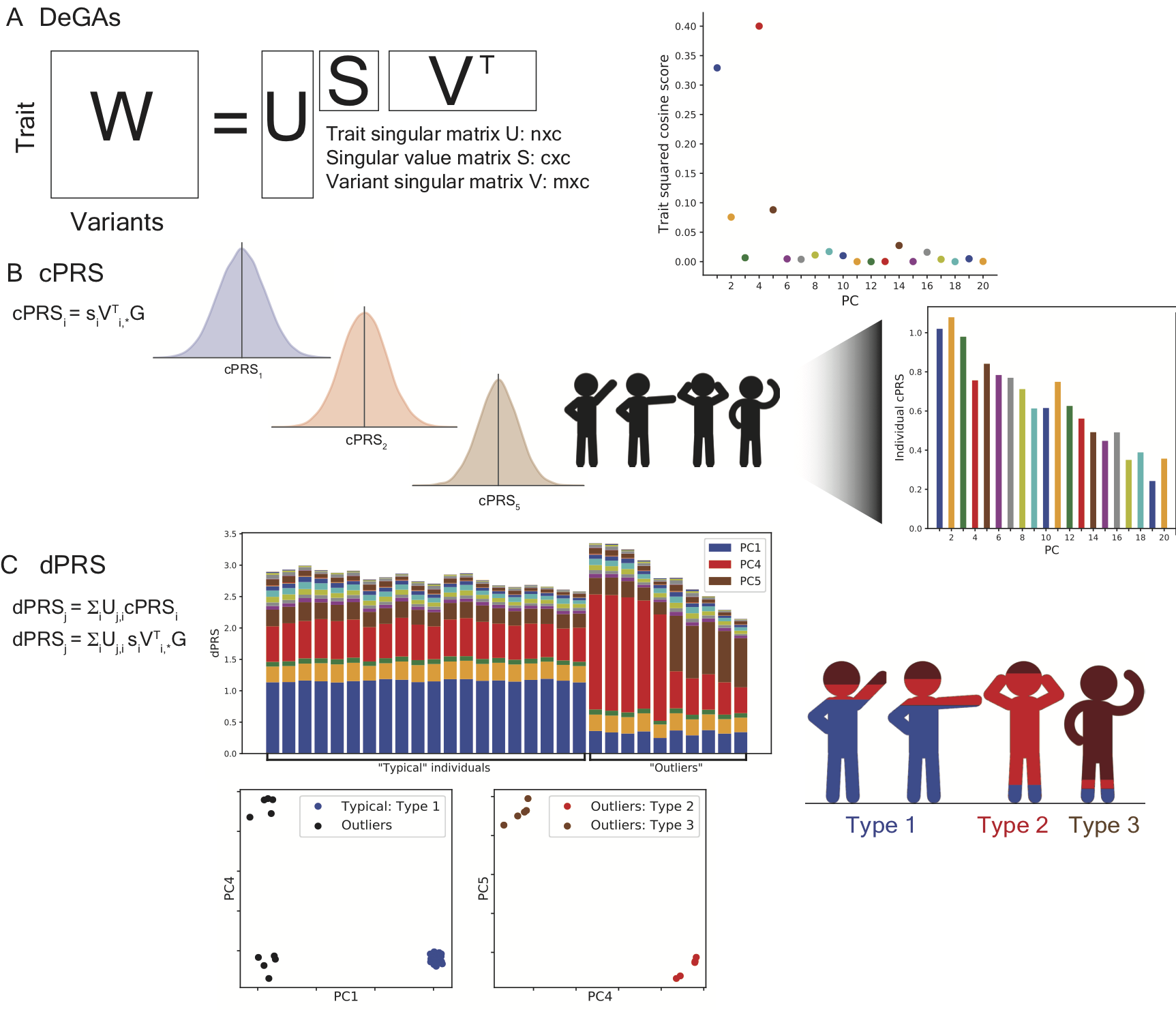
Reference: M. Aguirre, Y. Tanigawa, G. Venkataraman, R. J. Tibshirani, T. Hastie, M. A. Rivas, Polygenic risk modeling with latent trait-related genetic components. bioRxiv, 808675 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/808675
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
In this study led by Emily Flynn, we discovered a surprising sex-specificity in the genetics of testosterone. Yosuke performed polygenic risk score (PRS) analysis and demonstrated that PRS models trained for each sex show improvements in predictive accuracy.
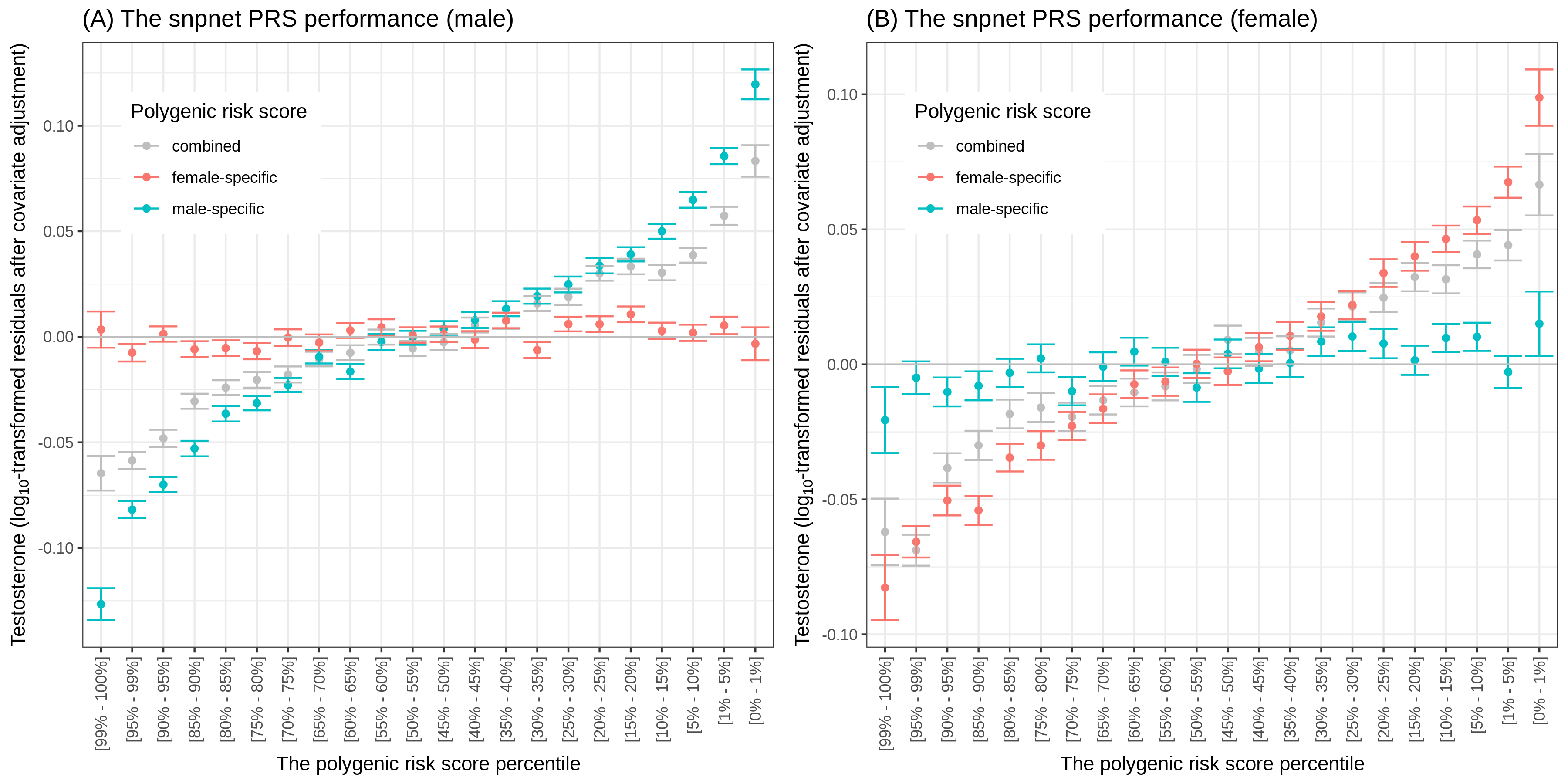
Reference: E. Flynn, Y. Tanigawa, F. Rodriguez, R. B. Altman, N. Sinnott-Armstrong, M. A. Rivas, Sex-specific genetic effects across biomarkers. bioRxiv, 837021 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/837021
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2019
Reference: C. DeBoever, A. J. Venkatakrishnan, J. M. Paggi, F. M. Heydenreich, S.-A. Laurin, M. Masureel, Y. Tanigawa, G. Venkataraman, M. Bouvier, R. Dror, M. A. Rivas, Medical relevance of common protein-altering variants in GPCR genes across 337,205 individuals in the UK Biobank study. bioRxiv, 2019.12.13.876250 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1101/2019.12.13.876250
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2020
We propose an extension of BASIL/snpnet alrogirhm to fit L1 penalized Cox proportional hazards model using a large-scale dataset from a genotyped cohort. We present its application to 300+ time-to-event traits in UK Biobank.
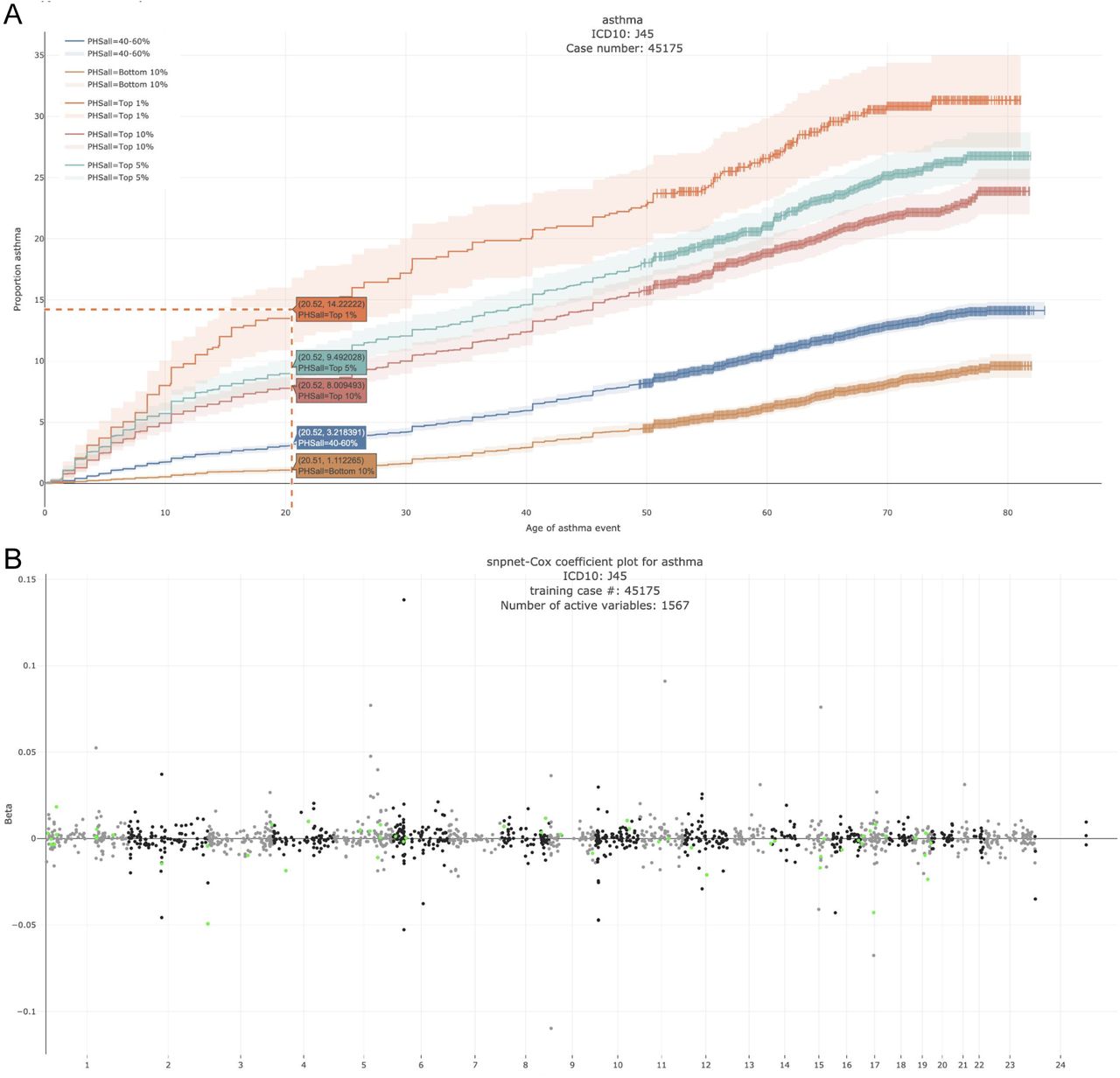
Reference: R. Li, C. Chang, J. M. Justesen, Y. Tanigawa, J. Qian, T. Hastie, M. A. Rivas, R. J. Tibshirani, Fast Lasso method for Large-scale and Ultrahigh-dimensional Cox Model with applications to UK Biobank. bioRxiv, 2020.01.20.913194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.20.913194
Preprint posted on Preprints.org, 2020
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, M. Rivas, Initial Review and Analysis of COVID-19 Host Genetics and Associated Phenotypes (2020). https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202003.0356.v1
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2020
This preprint is now published in Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine!
Reference: A. Cordova-Palomera, C. Tcheandjieu, J. Fries, P. Varma, V. Chen, M. Fiterau, K. Xiao, H. Tejeda, B. Keavney, H. Cordell, Y. Tanigawa, G. Venkataraman, M. Rivas, C. Re, E. Ashley, J. R. Priest, Cardiac imaging of aortic valve area from 26,142 UK Biobank participants reveal novel genetic associations and shared genetic comorbidity with multiple disease phenotypes. medRxiv, 2020.04.09.20060012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.09.20060012
Published in PLOS Genetics, 2020
From the analysis of more than 500,000 individuals in population cohorts, we identified rare protein-altering variants in ANGPTL7 that reduce the risk of glaucoma. One of the alleles reported in the study (220C) is highly (50x +) enriched in the Finnish population, highlighting the power of the founder population with prior a bottlenecking event in genetic discovery. With the comprehensive health information in the two studied cohorts, we assess the potential impact of the rare variants on a spectrum of human disorders. We did not find any severe medical consequences. Our results indicate that ANGPTL7 is a safe and effective therapeutic target for glaucoma.
This paper was highlighted as Editors’ Choice in Science.
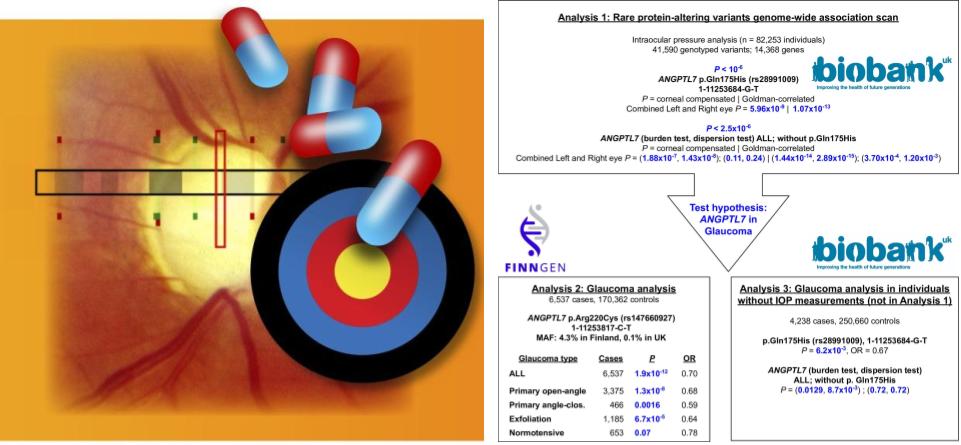
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, M. Wainberg, J. Karjalainen, T. Kiiskinen, G. Venkataraman, S. Lemmelä, J. A. Turunen, R. R. Graham, A. S. Havulinna, M. Perola, A. Palotie, FinnGen, M. J. Daly, M. A. Rivas, Rare protein-altering variants in ANGPTL7 lower intraocular pressure and protect against glaucoma. PLOS Genetics. 16, e1008682 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008682
Published in The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2020
Large-scale population-based genotyped biobanks with dense phenotypic information provide opportunities for genetic analysis at scale. However, the heterogeneous phenotypic data sources in such biobanks present challenges in disease case ascertainment. Here, we evaluated the consistency of genetic associations identified from hospital records, questionnaire responses, and family history of diseases using genetic parameters, such as genetic correlation. We also showed the utility of combining the unstructured and heterogeneous data sources to improve the power of genetic analysis.
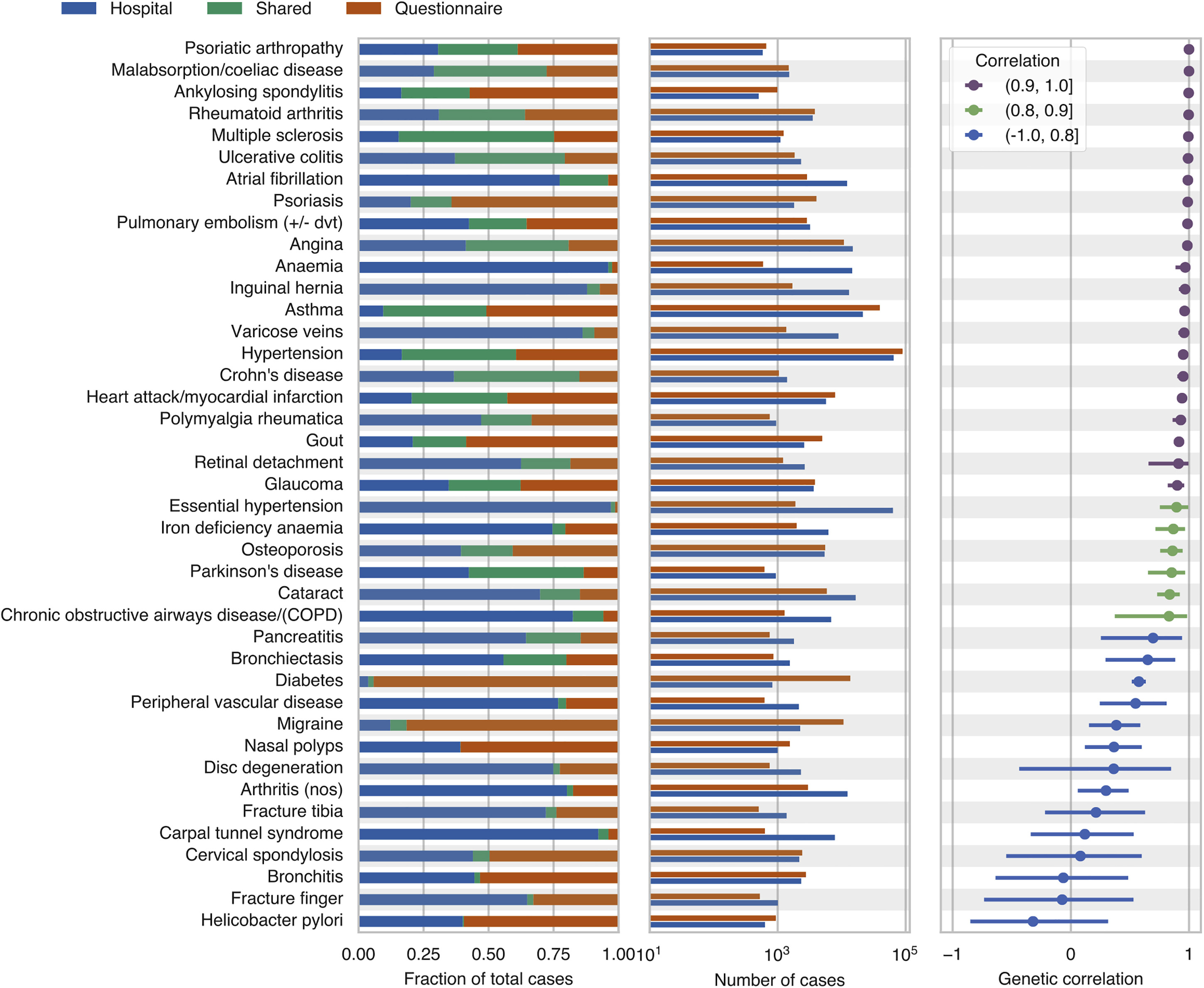
Reference: C. DeBoever, Y. Tanigawa, M. Aguirre, G. McInnes, A. Lavertu, M. A. Rivas, Assessing Digital Phenotyping to Enhance Genetic Studies of Human Diseases. Am J Hum Genet. 106(5), 611-622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.03.007
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2020
We characterized the genetic associations between HLA allelotypes and comprehensive human disease phenotypes in UK Biobank.
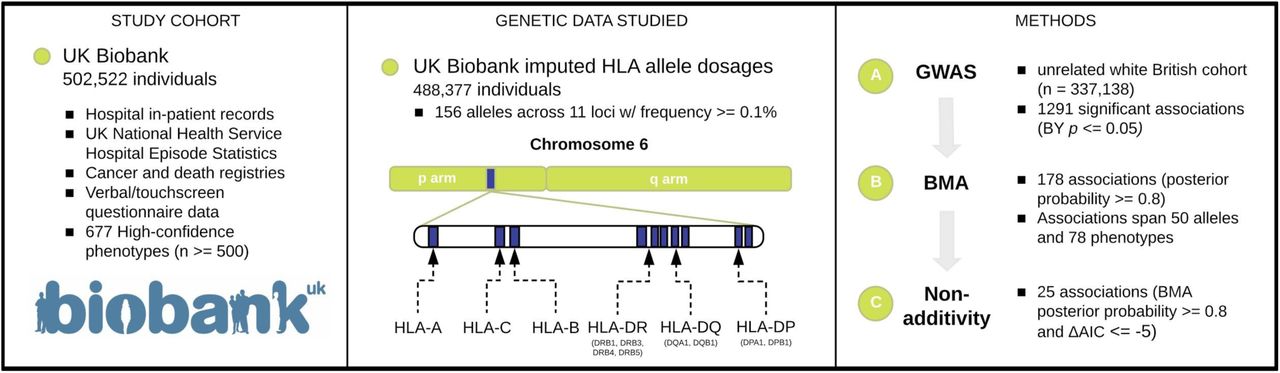
Reference: G. R. Venkataraman, J. E. Olivieri, C. DeBoever, Y. Tanigawa, J. M. Justesen, M. A. Rivas, Pervasive additive and non-additive effects within the HLA region contribute to disease risk in the UK Biobank. bioRxiv, 2020.05.28.119669 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.28.119669
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2020
In this study led by Junyang Qian, we present a method to fit sparse multi-variate and multi-response regression model. When demonstrate the application to the UK Biobank biomarker traits, where we investigated the latent structure of regression coefficients using biplot representation.
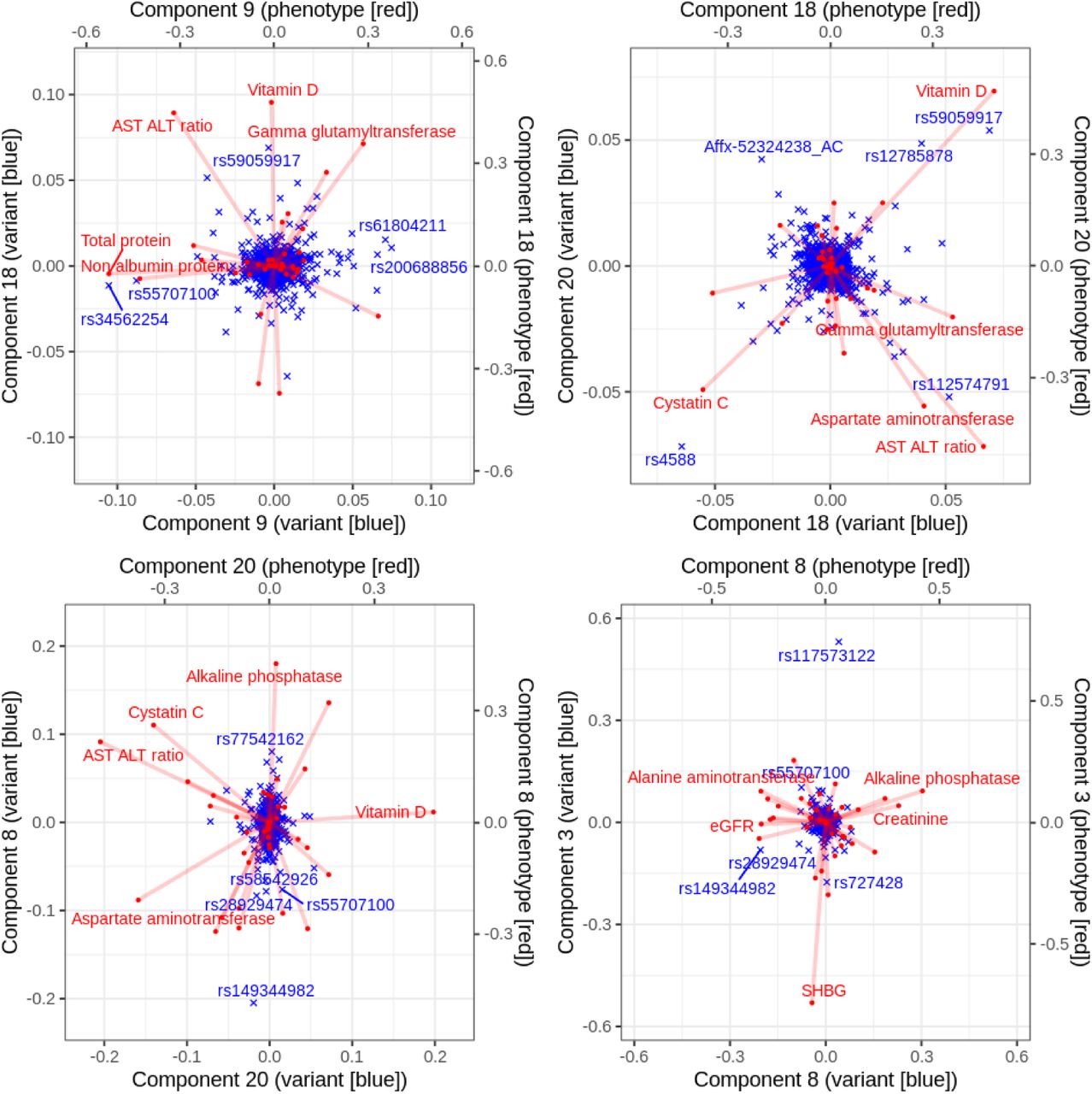
Reference: J. Qian, Y. Tanigawa, R. Li, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, T. Hastie, Large-Scale Sparse Regression for Multiple Responses with Applications to UK Biobank. bioRxiv, 2020.05.30.125252 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.30.125252
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2020
This preprint is now published in Bioinformatics!
Reference: R. Li, Y. Tanigawa, J. M. Justesen, J. Taylor, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, Survival Analysis on Rare Events Using Group-Regularized Multi-Response Cox Regression. bioRxiv, 2020.06.21.163675 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.21.163675
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2020
In this pre-print, we describe a new method to generate host and pathogen genomic data.
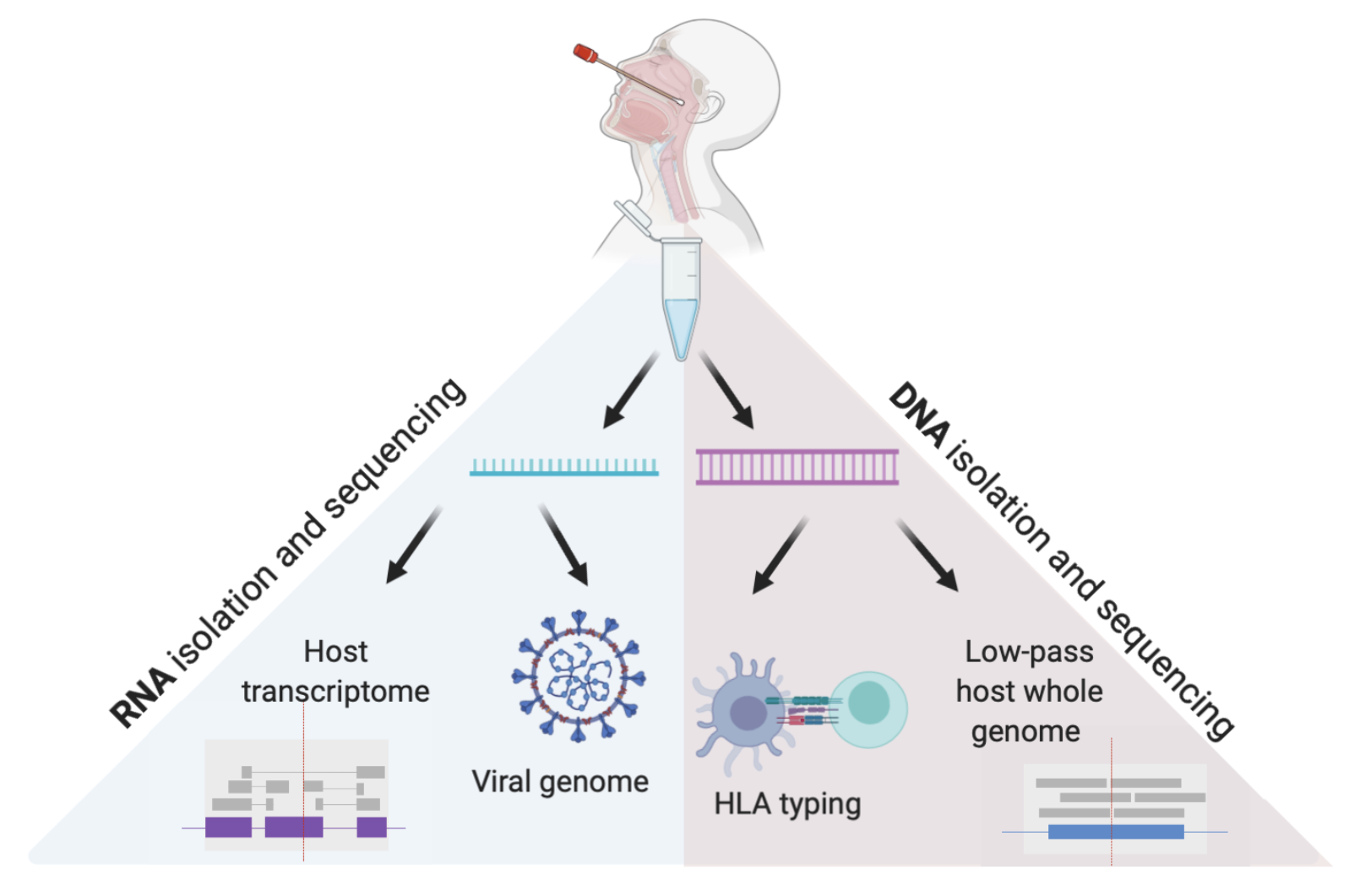
Reference: J. E. Gorzynski*, H. N. D. Jong*, D. Amar, C. R. Hughes, A. Ioannidis, R. Bierman, D. Liu, Y. Tanigawa, A. Kistler, J. Kamm, J. Kim, L. Cappello, N. F. Neff, S. Rubinacci, O. Delaneua, M. J. Shoura, K. Seo, A. Kirillova, A. Raja, S. Sutton, C. Huang, M. K. Sahoo, K. C. Mallempati, G. Montero-Martin, K. Osoegawa, N. Watson, N. Hammond, R. Joshi, M. Fernandez-Vina, J. W. Christle, M. T. Wheeler, P. Febbo, K. Farh, G. Schroth, F. Desouza, J. Palacios, J. Salzman, B. A. Pinsky, M. A. Rivas, C. D. Bustamante, E. A. Ashley, V. N. Parikh, High-throughput SARS-CoV-2 and host genome sequencing from single nasopharyngeal swabs, medRxiv, 2020.07.27.20163147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.27.20163147
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2020
Statin is a commonly used drug for high cholesterol. Physicians adjust the type and dose of statin based on the observed response to the treatment. To investigate the role of genetics, we performed genome-wide association scan to identify genetic variants associated with statin selection. When we investigated the identified variants in LPA and APOE, we found that the carriers of those variants more likely to be on a higher dose of statin.
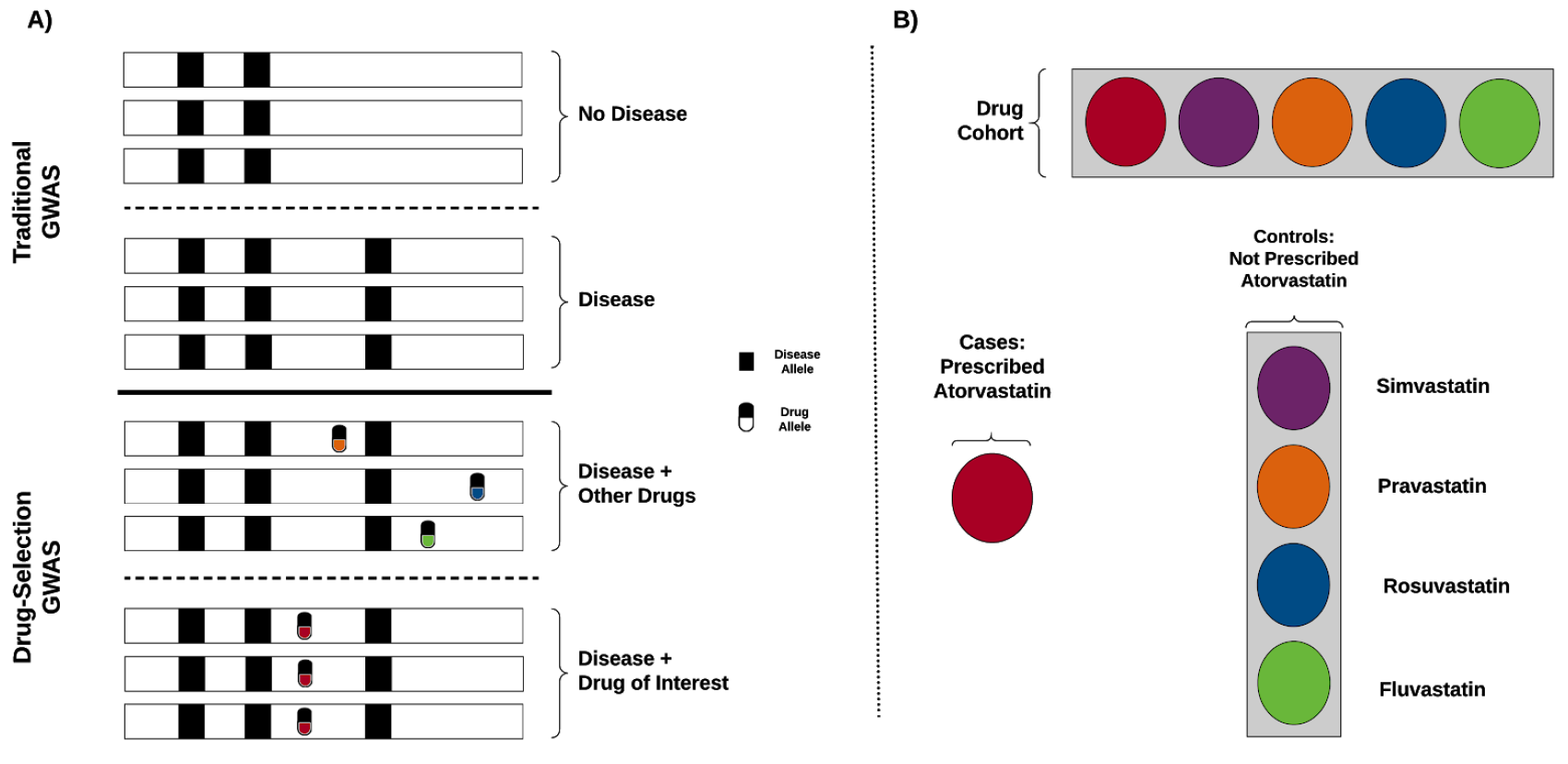
Reference: A. Lavertu*, G. M. McInnes*, Y. Tanigawa, R. B. Altman, M. A. Rivas, LPA and APOE are associated with statin selection in the UK Biobank. bioRxiv, 2020.08.28.272765 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.28.272765
Published in European Journal of Human Genetics, 2020
In this study led by Emily Flynn, we discovered a surprising sex-specificity in the genetics of testosterone. Yosuke performed the polygenic risk score (PRS) analysis and demonstrated that PRS models trained for each sex improve predictive accuracy.

Reference: E. Flynn, Y. Tanigawa, F. Rodriguez, R. B. Altman, N. Sinnott-Armstrong, M. A. Rivas, Sex-specific genetic effects across biomarkers. Eur J Hum Genet, 29(1), 154-163 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-00712-w (full text)
Published in Biostatistics, 2020
We propose extending the BASIL/snpnet algorithm to fit the L1 penalized Cox proportional hazards model using a large-scale dataset from a genotyped cohort. We present its application to 300+ time-to-event traits in UK Biobank.

Reference: R. Li, C. Chang, J. M. Justesen, Y. Tanigawa, J. Qiang, T. Hastie, M. A. Rivas, R. Tibshirani, Fast Lasso method for large-scale and ultrahigh-dimensional Cox model with applications to UK Biobank. Biostatistics. 23(2), 522-540 (2020). https://doi.org/doi:10.1093/biostatistics/kxaa038
Published in PLOS Genetics, 2020
In this project led by Junyang Qian, we developed BASIL, a novel algorithm to fit large-scale L1 penalized (Lasso) regression model using an iterative procedure, and implemented R snpnet package specially designed for genetic data. We demonstrate the ability of this approach in an application to UK Biobank dataset.
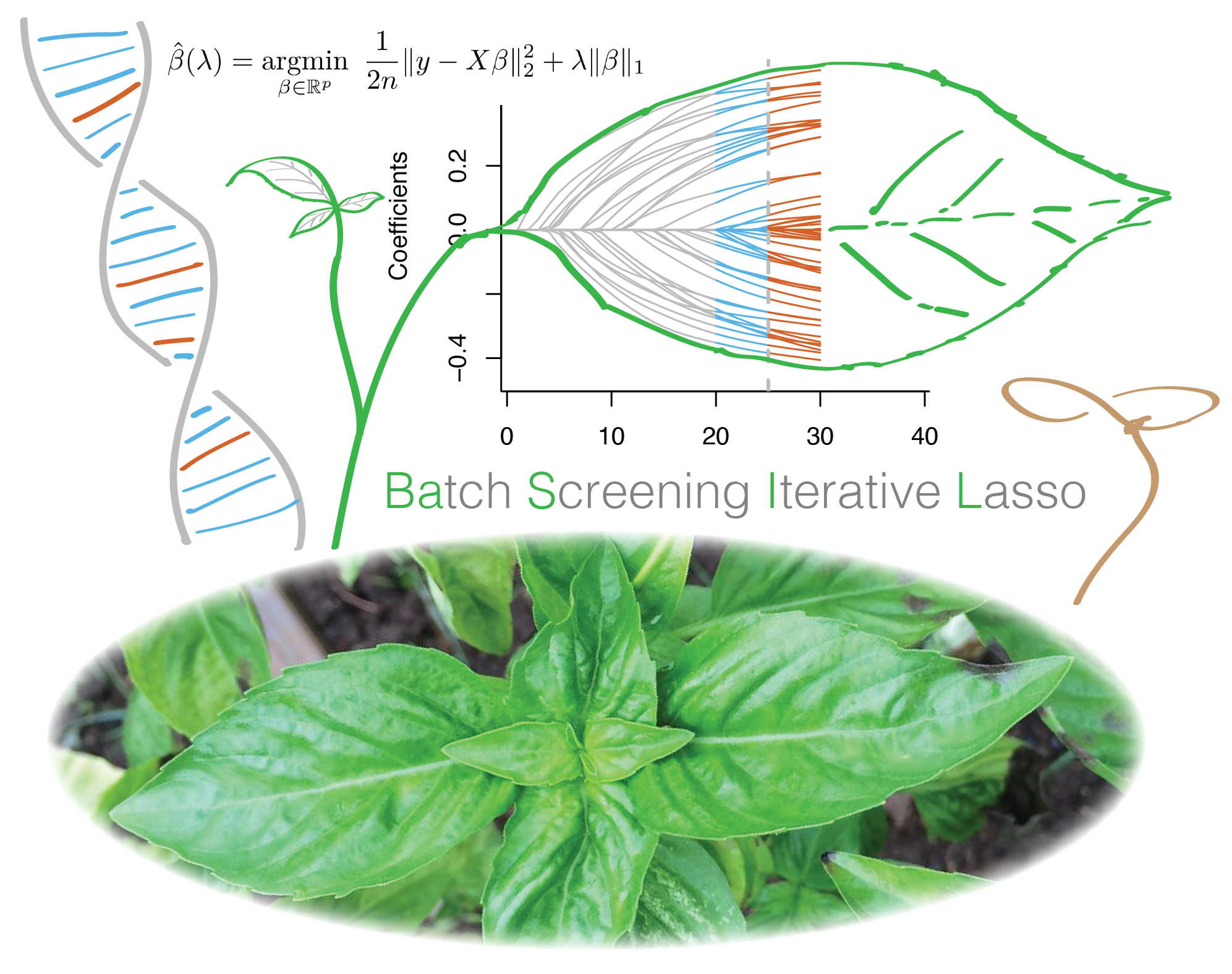
Reference: J. Qian, Y. Tanigawa, W. Du, M. Aguirre, C. Chang, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, T. Hastie, A fast and scalable framework for large-scale and ultrahigh-dimensional sparse regression with application to the UK Biobank. PLoS Genet. 16, e1009141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1009141
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2020
Using a set of GWAS summary statistics of diseases characterized from both European (UK Biobank and FinnGen) and East Asian (Biobank Japan) populations, we dissected latent DeGAs components of multi-ethnic association summary statistics. We annotated each component by pathway and cell-type enrichment as well as projection of metabolomic and biomarker summary statistics. We demonstrate how can we use such trans-ethnic annotated latent components to classify diseases based on their genetic basis.

Reference: S. Sakaue*, M. Kanai*, Y. Tanigawa, J. Karjalainen, M. Kurki, S. Koshiba, A. Narita, T. Konuma, K. Yamamoto, M. Akiyama, K. Ishigaki, A. Suzuki, K. Suzuki, W. Obara, K. Yamaji, K. Takahashi, S. Asai, Y. Takahashi, T. Suzuki, N. Sinozaki, H. Yamaguchi, S. Minami, S. Murayama, K. Yoshimori, S. Nagayama, D. Obata, M. Higashiyama, A. Masumoto, Y. Koretsune, F. Gen, K. Ito, C. Terao, T. Yamauchi, I. Komuro, T. Kadowaki, G. Tamiya, M. Yamamoto, Y. Nakamura, M. Kubo, Y. Murakami, K. Yamamoto, Y. Kamatani, A. Palotie, M. A. Rivas, M. Daly, K. Matsuda, Y. Okada, A global atlas of genetic associations of 220 deep phenotypes. medRxiv, 2020.10.23.20213652 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.23.20213652
Published in Circ Genom Precis Med., 2020
Reference: A. Cordova-Palomera, C. Tcheandjieu, J. Fries, P. Varma, V. Chen, M. Fiterau, K. Xiao, H. Tejeda, B. Keavney, H. Cordell, Y. Tanigawa, G. Venkataraman, M. Rivas, C. Re, E. Ashley, J. R. Priest, Cardiac Imaging of Aortic Valve Area from 34,287 UK Biobank Participants Reveal Novel Genetic Associations and Shared Genetic Comorbidity with Multiple Disease Phenotypes. Circ Genom Precis Med. 13(6):e003014, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGEN.120.003014
Published in Nature Genetics, 2021
We characterized the genetics of 35 biomarkers in UK Biobank. We performed the association and fine-mapping analysis to prioritize the causal variants, constructed the polygenic risk score (PRS) models, and evaluated their medical relevance with causal inference and PRS-PheWAS. We demonstrate a new approach, called multi-PRS, to improve PRS by combining PRSs across traits.

Reference: N. Sinnott-Armstrong*, Y. Tanigawa*, D. Amar, N. J. Mars, C. Benner, M. Aguirre, G. R. Venkataraman, M. Wainberg, H. M. Ollila, T. Kiiskinen, A. S. Havulinna, J. P. Pirruccello, J. Qian, A. Shcherbina, FinnGen, F. Rodriguez, T. L. Assimes, V. Agarwala, R. Tibshirani, T. Hastie, S. Ripatti, J. K. Pritchard, M. J. Daly, M. A. Rivas, Genetics of 35 blood and urine biomarkers in the UK Biobank. Nat Gen. 53(2), 185-194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-020-00757-z (full text)
Published in European Journal of Human Genetics, 2021
Polygenic risk score (PRS) has been proposed for disease risk prediction with potential clinical relevance for some traits, but its personalized interpretation is generally difficult, especially when there exist disease subtypes driven by different genetic components. In this study led by Matthew Aguirre, we introduce dPRS (DeGAs-PRS) as an extension of Decomposition of Genetic Associations (DeGAs) to decompose the polygenic risk of individuals into latent components of genetic associations characterized from hundreds of thousands of traits.

Reference: M. Aguirre, Y. Tanigawa, G. R. Venkataraman, R. Tibshirani, T. Hastie, M. A. Rivas, Polygenic risk modeling with latent trait-related genetic components. Eur J Hum Genet. 29(7), 1071-1081 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-021-00813-0 (full text)
Published in Bioinformatics, 2021
In this paper led by Ruilin Li, we describe a new method to fit a sparse Cox Model for multiple time-to-event phenotypes from a large-scale (> 1 million features) genetic dataset.
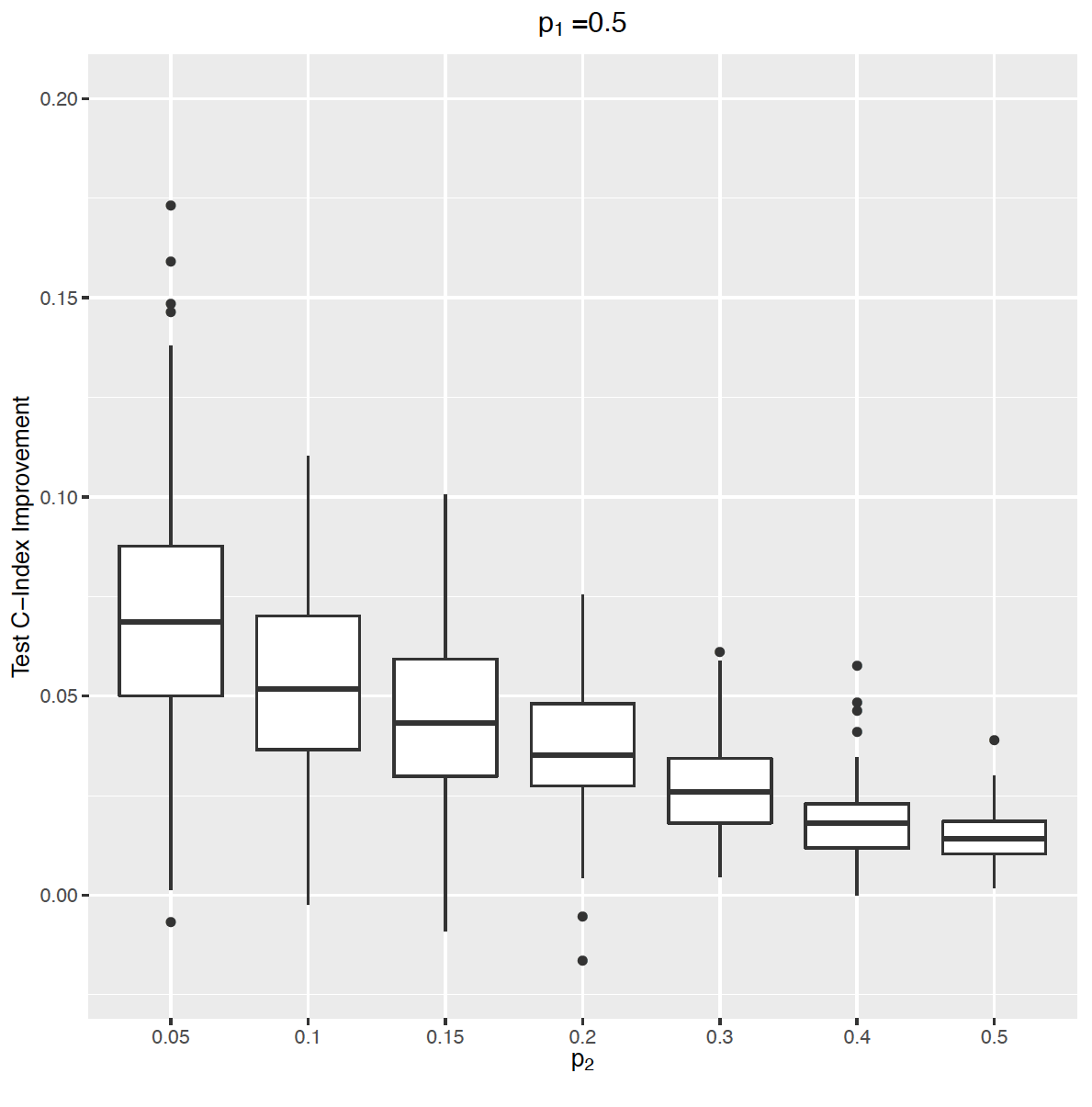
Reference: R. Li, Y. Tanigawa, J. M. Justesen, J. Taylor, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, Survival Analysis on Rare Events Using Group-Regularized Multi-Response Cox Regression. Bioinformatics 37(23), 4437-4443 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab095
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2021
In this project led by Ruilin Li, we improved the efficiency of the R snpnet package by taking advantage of the sparsity-aware compact on-memory representation of the genotype data matrix.
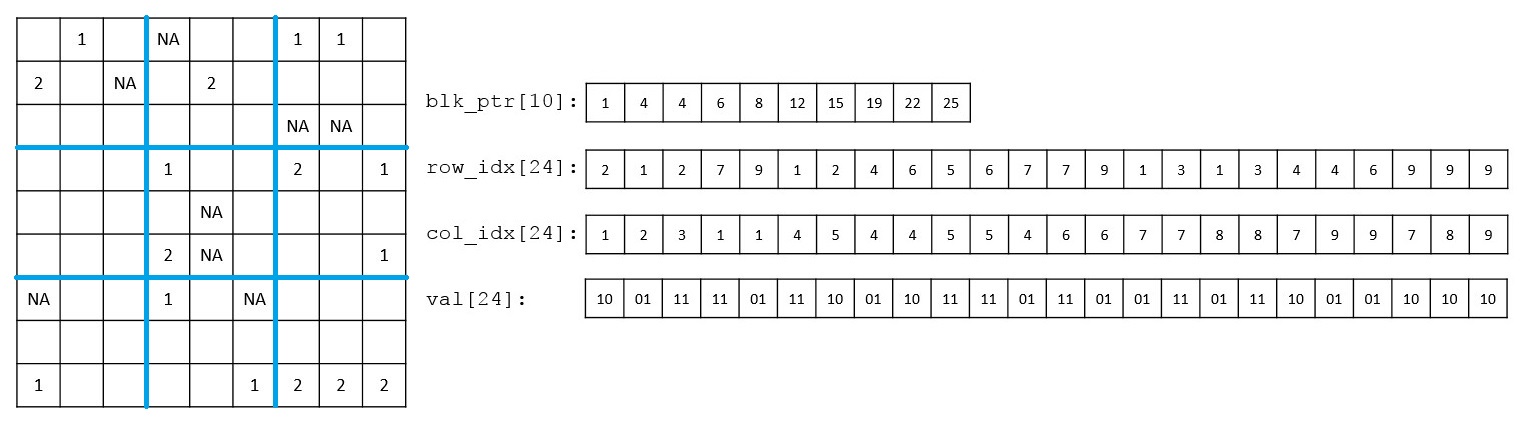
Reference: R. Li, C. Chang, Y. Tanigawa, B. Narasimhan, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, Fast Numerical Optimization for Genome Sequencing Data in Population Biobanks. bioRxiv, 2021.02.14.431030 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.14.431030
Published in JSBi Bioinformatics Review, 2021
[invited review written in Japanese] 日本語総説の執筆の機会をいただき、ゲノムワイド相関解析(GWAS)、ポリジェニック・リスク・スコア(polygenic risk score)、高次元データセットでの正則化つきの回帰モデル(penalized regression、Lasso 回帰など)に関する人類統計遺伝学の解析手法について執筆しました。
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, Large-scale human genetic statistical inference with multiple phenotypes. JSBi Bioinformatics Review, 1(2), 47-59 (2021). https://doi.org/10.11234/jsbibr.2021.4
Published in Bioinformatics, 2021
In this paper led by Ruilin Li, we describe memory-efficient implementation of snpnet (sparse-snpnet and snpnet-v2).

Reference: R. Li, C. Chang, Y. Tanigawa, B. Narasimhan, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, Fast Numerical Optimization for Genome Sequencing Data in Population Biobanks. Bioinformatics 37(22), 4148-4155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab452 (full text)
Published in Nature, 2021
This consortia flagship manuscript has 2000+ authors. I have been fortunate to be part of the participating study to the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative.
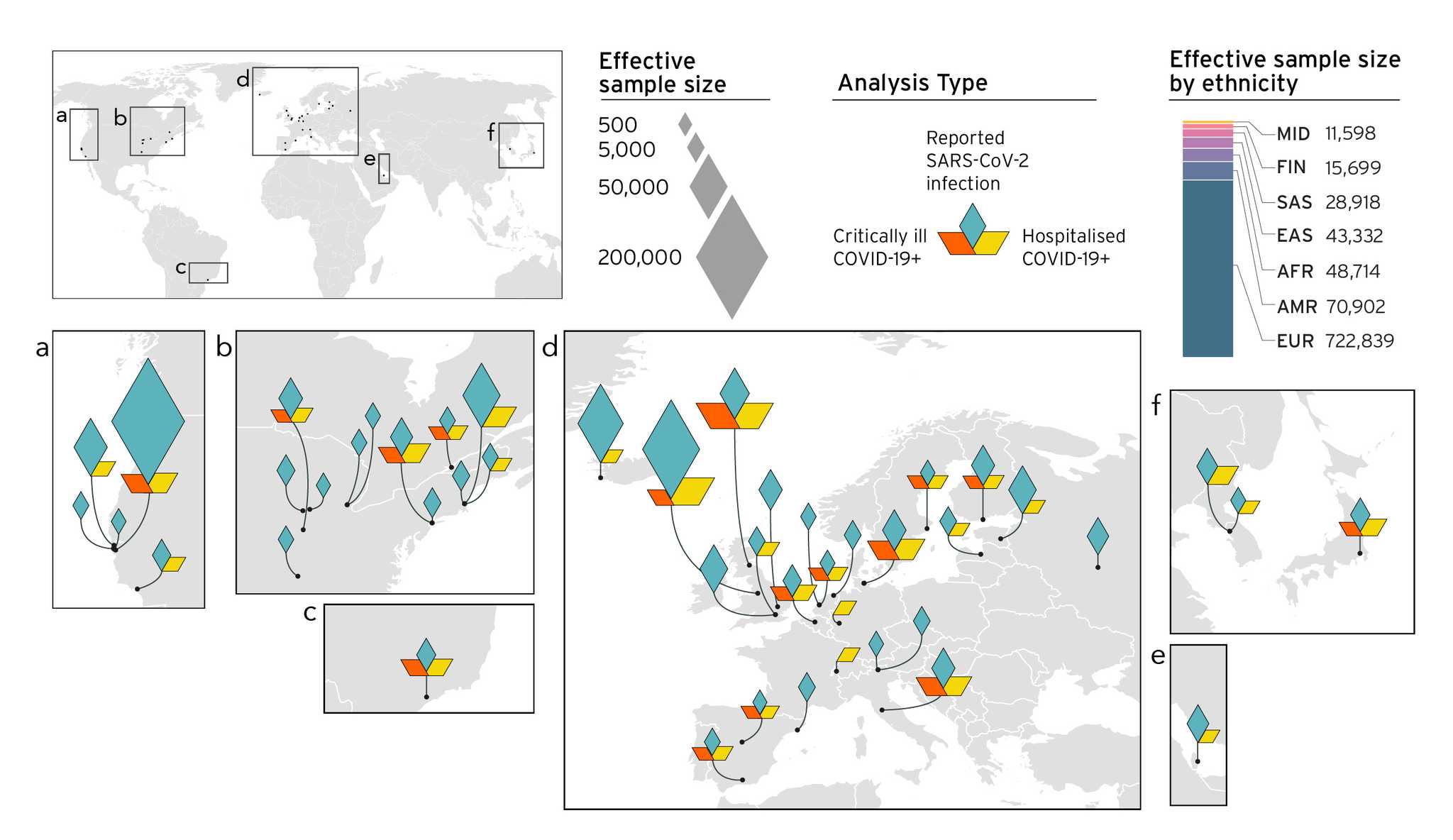
Reference: COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative, Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. Nature 600(7890), 472-477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03767-x
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2021
This preprint is now published in American Journal of Human Genetics!
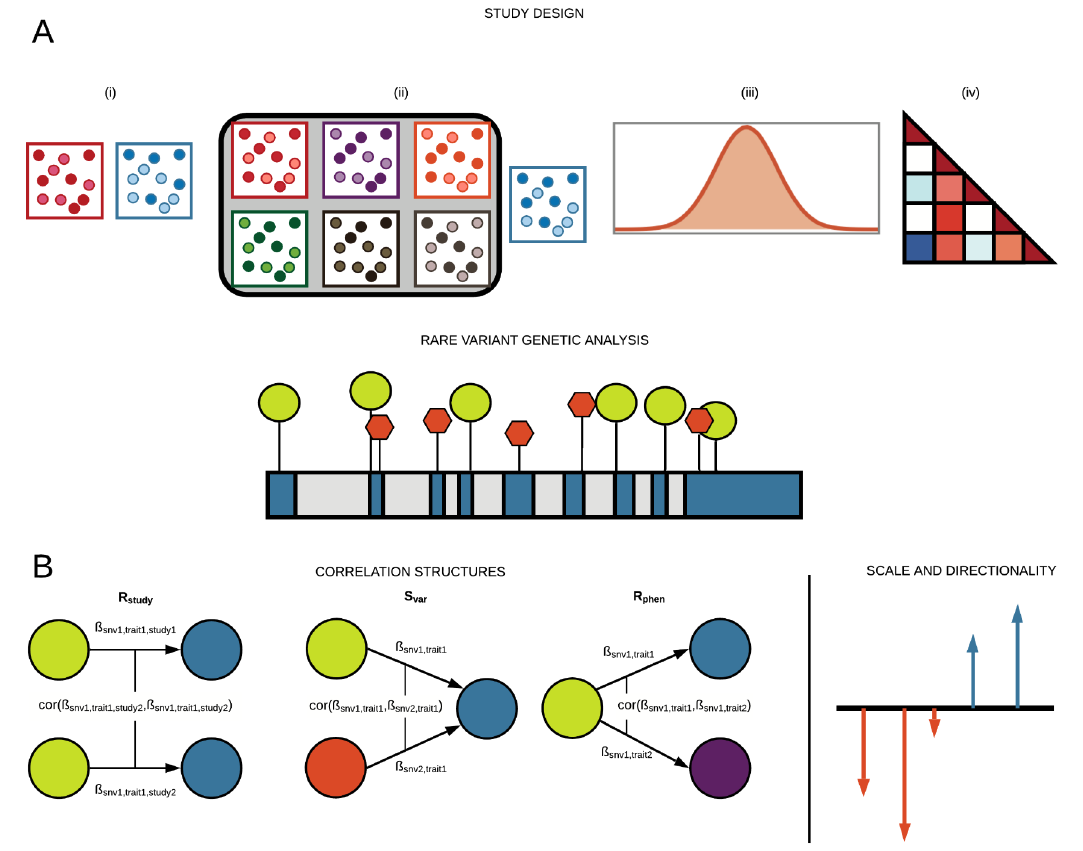
Reference: G. R. Venkataraman, C. DeBoever, Y. Tanigawa, M. Aguirre, A. G. Ioannidis, H. Mostafavi, C. C. A. Spencer, T. Poterba, C. D. Bustamante, M. J. Daly, M. Pirinen, M. A. Rivas, Bayesian model comparison for rare variant association studies. bioRxiv, 257162 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/257162
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2021
Reference: G. R. Venkataraman, Y. Tanigawa, M. Pirinen, M. A. Rivas, Bayesian mixture model for clustering rare-variant effects in human genetic studies. bioRxiv, 2021.08.03.454967 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.03.454967
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2021
This preprint is now published in Nature Communications!
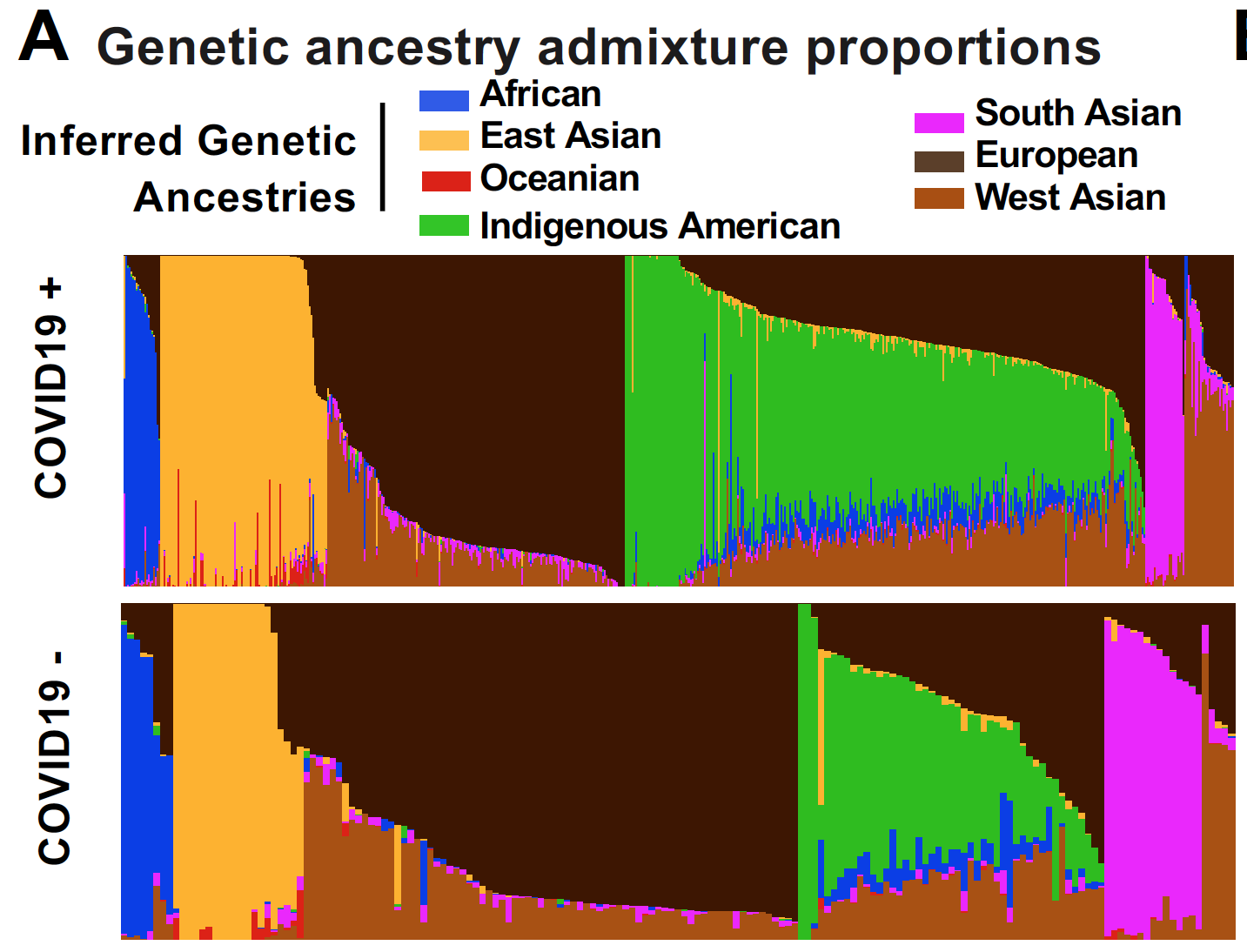
Reference: V. N. Parikh, A. G. Ioannidis, D. Jimenez-Morales, J. E. Gorzynski, H. N. D. Jong, X. Liu, J. Roque, V. P. Cepeda-Espinoza, K. Osoegawa, C. Hughes, S. C. Sutton, N. Youlton, R. Joshi, D. Amar, Y. Tanigawa, D. Russo, J. Wong, J. T. Lauzon, J. Edelson, D. M. Montserrat, Y. Kwon, S. Rubinacci, O. Delaneau, L. Cappello, J. Kim, M. J. Shoura, A. N. Raja, N. Watson, N. Hammond, E. Spiteri, K. C. Mallempati, G. Montero-Martin, J. Christle, J. Kim, A. Kirillova, K. Seo, Y. Huang, C. Zhao, S. Moreno-Grau, S. Hershman, K. P. Dalton, J. Zhen, J. Kamm, K. Bhatt, A. Isakova, M. Morri, T. Ranganath, C. A. Blish, A. J. Rogers, K. Nadeau, S. Yang, A. Blomkalns, R. OHara, N. F. Neff, C. DeBoever, S. Szalma, M. T. Wheeler, K. Farh, G. P. Schroth, P. Febbo, F. deSouza, M. Fernandez-Vina, A. Kistler, J. Palacios, B. A. Pinsky, C. D. Bustamante, M. A. Rivas, E. A. Ashley, Deconvoluting complex correlates of COVID19 severity with local ancestry inference and viral phylodynamics: Results of a multiomic pandemic tracking strategy. medRxiv 2021.08.04.21261547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.04.21261547
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2021
We performed a systematic assessment of the predictive performance of PRS models across >1,500 traits in UK Biobank and report 813 PRS models with significant predictive performance.
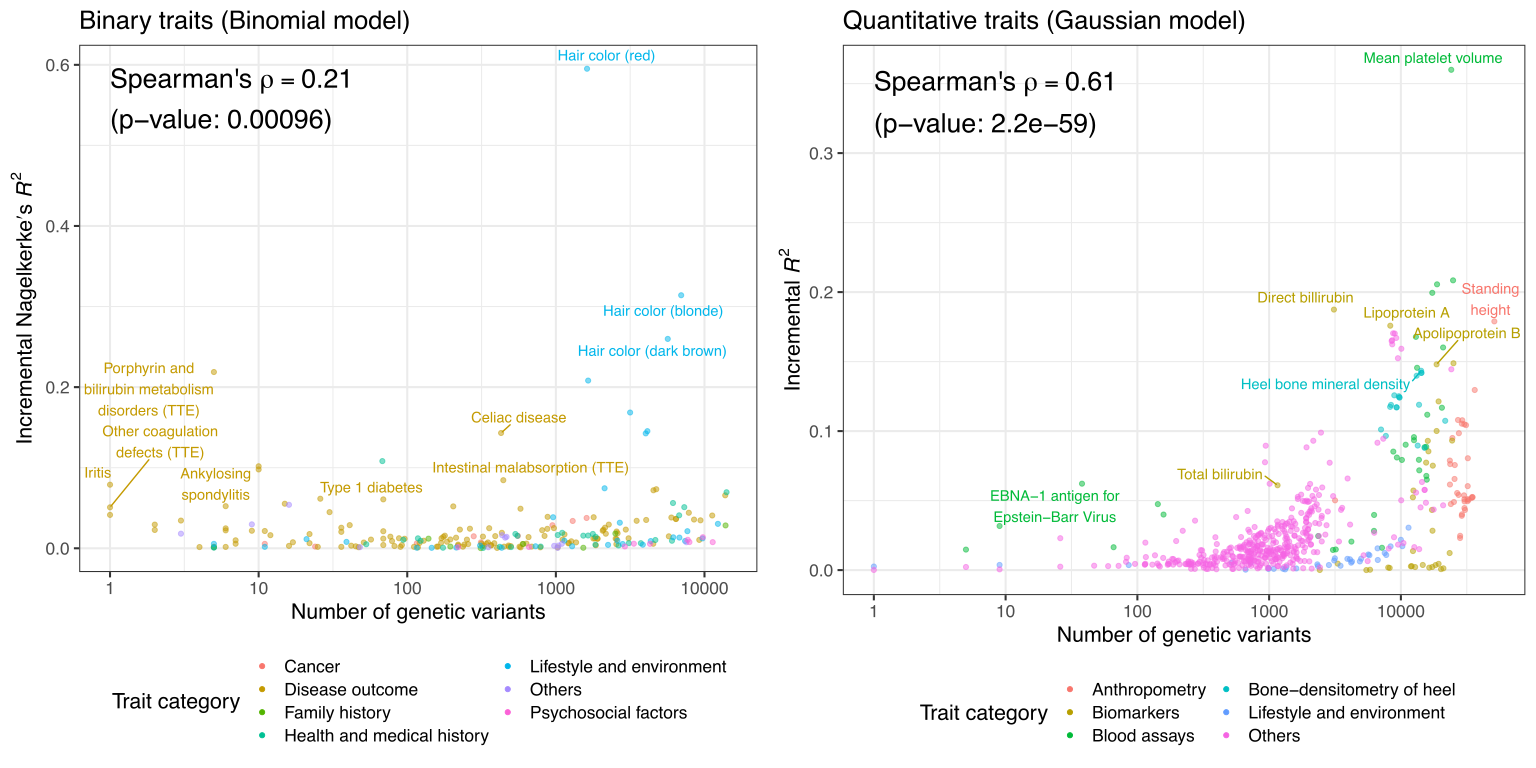
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, J. Qian, G. R. Venkataraman, J. M. Justesen, R. Li, R. Tibshirani, T. Hastie, M. A. Rivas, Significant Sparse Polygenic Risk Scores across 813 traits in UK Biobank. medRxiv 2021.09.02.21262942 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.02.21262942
Published in Lipids in Health and Disease, 2021
We examined the causal relationship between the genetically increased triglycerides and the risk of coronary artery diseases in Asian Indians.
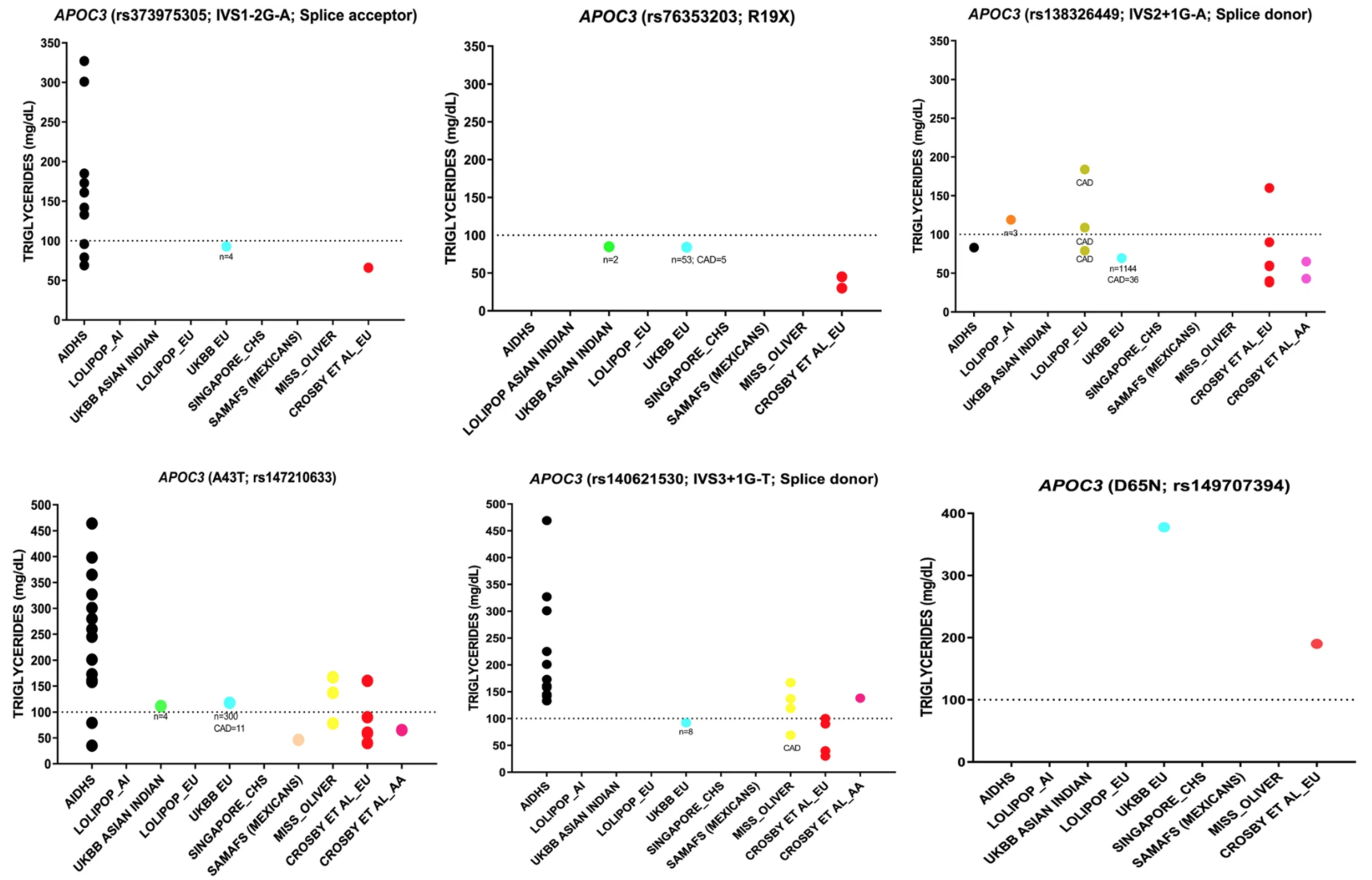
Reference: S. Goyal, Y. Tanigawa, W. Zhang, J. Chai, M. Almeida, X. Sim, M. Lerner, J. Chainakul, J. G. Ramiu, C. Seraphin, B. Apple, A. Vaughan, J. Muniu, J. Peralta, D. M. Lehman, S. Ralhan, G. S. Wander, J. R. Singh, N. K. Mehra, E. Sidorov, M. D Peyton, P. R. Blackett, J. E. Curran, E. S. Tai, R. van Dam, C. Cheng, R. Duggirala, J. Blangero, J. C. Chambers, C. Sabanayagam, J. S. Kooner, M. A. Rivas, C. E. Aston, D. Sanghera, APOC3 genetic variation, serum triglycerides, and risk of coronary artery disease in Asian Indians, Europeans, and other ethnic groups. Lipids Health Dis (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-021-01531-8
Published in Nature Genetics, 2021
Using a set of GWAS summary statistics of diseases characterized from both European (UK Biobank and FinnGen) and East Asian (Biobank Japan) populations, we dissected latent DeGAs components of multi-ethnic association summary statistics. We annotated each component by pathway and cell-type enrichment as well as projection of metabolomic and biomarker summary statistics. We demonstrate how we can use such trans-ethnic annotated latent components to classify diseases based on their genetic basis.
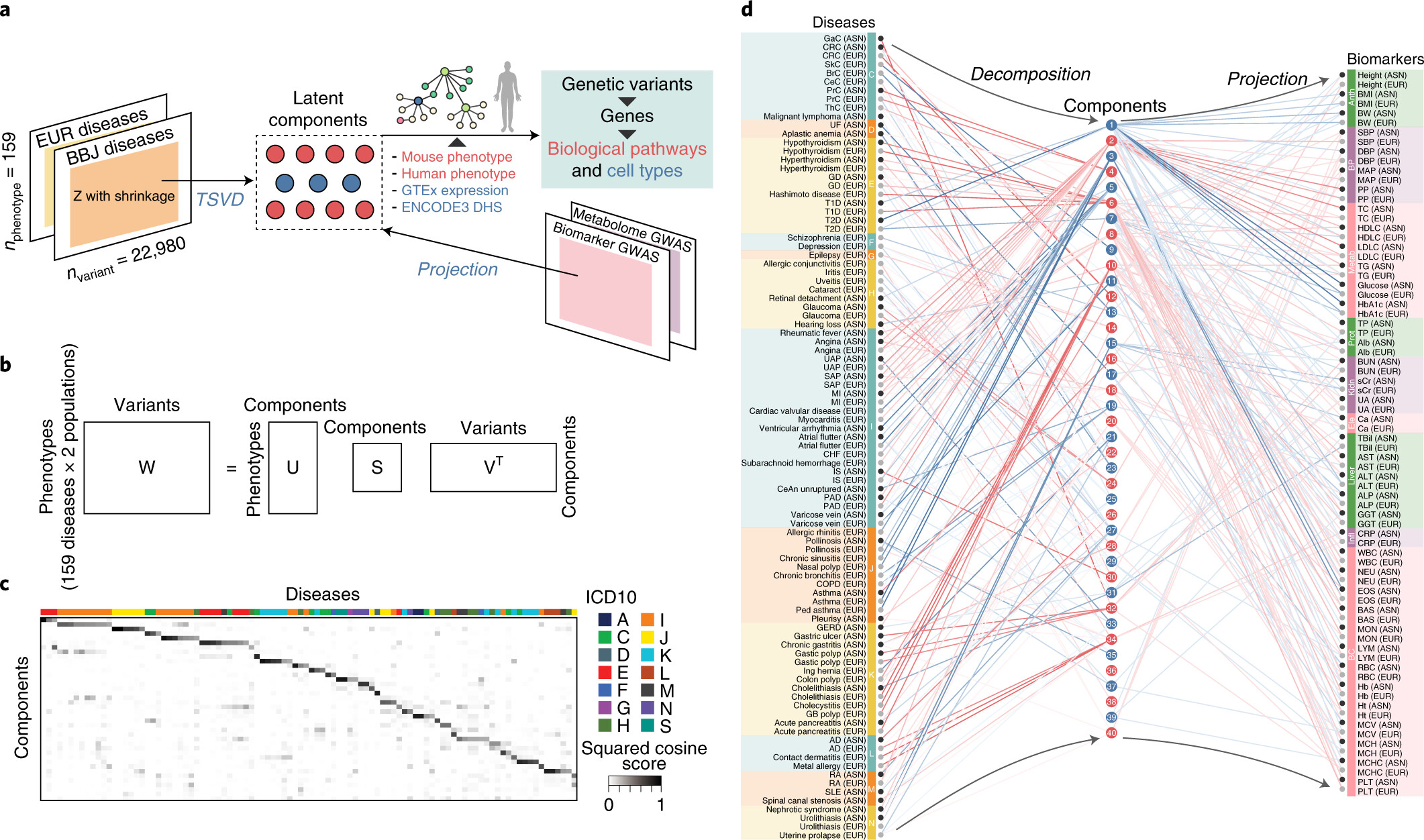
Reference: S. Sakaue*, M. Kanai*, Y. Tanigawa, J. Karjalainen, M. Kurki, S. Koshiba, A. Narita, T. Konuma, K. Yamamoto, M. Akiyama, K. Ishigaki, A. Suzuki, K. Suzuki, W. Obara, K. Yamaji, K. Takahashi, S. Asai, Y. Takahashi, T. Suzuki, N. Sinozaki, H. Yamaguchi, S. Minami, S. Murayama, K. Yoshimori, S. Nagayama, D. Obata, M. Higashiyama, A. Masumoto, Y. Koretsune, F. Gen, K. Ito, C. Terao, T. Yamauchi, I. Komuro, T. Kadowaki, G. Tamiya, M. Yamamoto, Y. Nakamura, M. Kubo, Y. Murakami, K. Yamamoto, Y. Kamatani, A. Palotie, M. A. Rivas, M. Daly, K. Matsuda, Y. Okada, A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat Gen. 53(10), 1415-1424 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00931-x (full text)
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2021
Reference: J. Yang*, M. Vamvini*, P. Nigro*, L.-L. Ho, K. Galani, M. Alvarez, Y. Tanigawa, M. Laakso, L. Agudelo, P. Pajukanta, R. Middelbeek, K. Grove, L. Goodyear, M. Kellis, Single-cell dissection of obesity-exercise axis in adipose-muscle tissues. bioRxiv 2021.11.22.469622 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.22.469622
Published in Am J Hum Genet, 2021
Reference: G. R. Venkataraman, C. DeBoever, Y. Tanigawa, M. Aguirre, A. G. Ioannidis, H. Mostafavi, C. C. A. Spencer, T. Poterba, C. D. Bustamante, M. J. Daly, M. Pirinen, M. A. Rivas, Bayesian model comparison for rare-variant association studies. Am J Hum Genet. 108(12), 2354-2367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.11.005 (full text)
Published in PLOS Genetics, 2022
We performed a systematic assessment of the predictive performance of PRS models across >1,500 traits in UK Biobank and report 813 PRS models with significant predictive performance.

Reference: Y. Tanigawa, J. Qian, G. R. Venkataraman, J. M. Justesen, R. Li, R. Tibshirani, T. Hastie, M. A. Rivas, Significant Sparse Polygenic Risk Scores across 813 traits in UK Biobank. PLOS Genet. 18(3), e1010105 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1010105
Published in The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2022
Polygenic risk score (PRS), an approach to estimate genetic liability to complex traits by aggregating the effects across multiple genetic variants, has attracted increasing research interest. However, most existing PRSs focused on common variants, despite the well-established roles of specific rare genetic variants in common complex traits and diseases. To address this, we propose the independent outlier gene count (IOGC) score, an approach to aggregate the effects of rare variants that show expression outliers in a population-scale transcriptome sequencing study. We demonstrate that the high burden of the rare expression outlier variants on complex traits and the IOGC score improves polygenic prediction.
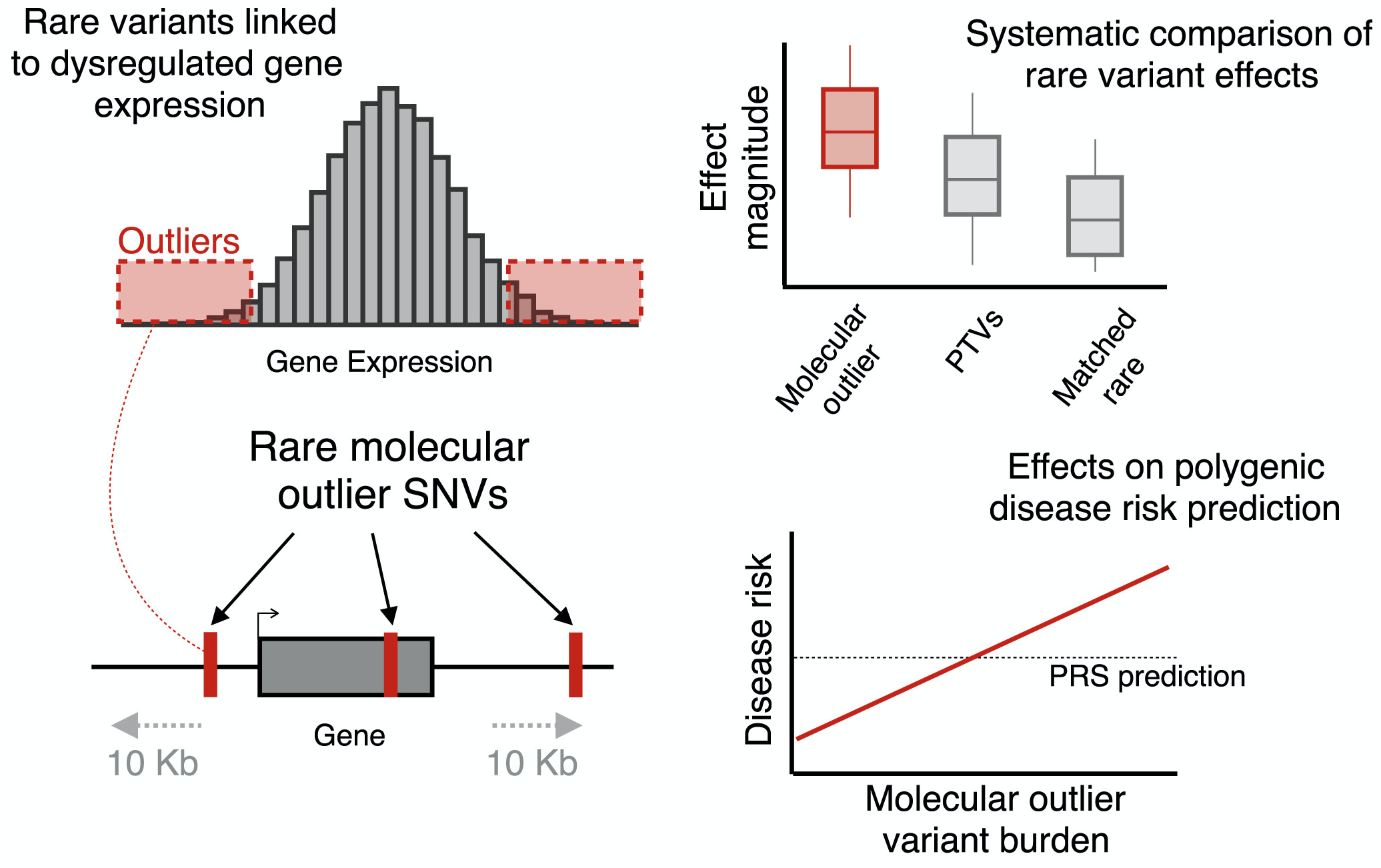
Reference: C. Smail, N. M. Ferraro, Q. Hui, M. G. Durrant, M. Aguirre, Y. Tanigawa, M. R. Keever-Keigher, A. S. Rao, J. M. Justesen, X. Li, M. J. Gloudemans, T. L. Assimes, C. Kooperberg, A. P. Reiner, J. Huang, C. J. O'Donnell, Y. V. Sun, Million Veteran Program, M. A. Rivas, S. B. Montgomery, Integration of rare expression outlier-associated variants improves polygenic risk prediction. Am J Hum Genet. 109(6), 1055-1064 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.04.015
Published in Ann. Appl. Stat., 2022
In this study led by Junyang Qian, we present a method to fit sparse multi-variate and multi-response regression model. When demonstrate the application to the UK Biobank biomarker traits, where we investigated the latent structure of regression coefficients using biplot representation.

Reference: J. Qian, Y. Tanigawa, R. Li, R. Tibshirani, M. A. Rivas, T. Hastie, Large-Scale Sparse Regression for Multiple Responses with Applications to UK Biobank. Ann. Appl. Stat. 16(3), 1891-1918 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1214/21-AOAS1575
Published in Nat Commun., 2022
Reference: V. N. Parikh*, A. G. Ioannidis*, D. Jimenez-Morales, J. E. Gorzynski, H. N. D. Jong, X. Liu, J. Roque, V. P. Cepeda-Espinoza, K. Osoegawa, C. Hughes, S. C. Sutton, N. Youlton, R. Joshi, D. Amar, Y. Tanigawa, D. Russo, J. Wong, J. T. Lauzon, J. Edelson, D. M. Montserrat, Y. Kwon, S. Rubinacci, O. Delaneau, L. Cappello, J. Kim, M. J. Shoura, A. N. Raja, N. Watson, N. Hammond, E. Spiteri, K. C. Mallempati, G. Montero-Martin, J. Christle, J. Kim, A. Kirillova, K. Seo, Y. Huang, C. Zhao, S. Moreno-Grau, S. Hershman, K. P. Dalton, J. Zhen, J. Kamm, K. Bhatt, A. Isakova, M. Morri, T. Ranganath, C. A. Blish, A. J. Rogers, K. Nadeau, S. Yang, A. Blomkalns, R. O’Hara, N. F. Neff, C. DeBoever, S. Szalma, M. T. Wheeler, C. Gates, K. Farh, G. P. Schroth, P. Febbo, F. deSouza, O. Cornejo, M. Fernandez-Vina, A. Kistler, J. Palacios, B. A. Pinsky, C. D. Bustamante, M. A. Rivas, E. A. Ashley, Deconvoluting complex correlates of COVID19 severity with a multi-omic pandemic tracking strategy. Nat Commun. 13, 5107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32397-8
Published in PLOS Comput Biol, 2022
We develop an ontology-guided approach to ranking tissue-/cell-type-specific transcription factors (TFs) from chromatin accessibility data.

Reference: Y. Tanigawa*, E. S. Dyer*, G. Bejerano, WhichTF is dominant in your open chromatin data? PLOS Comput Biol 18(8): e1010378. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010378
Published in Cell Metab., 2022
Reference: J. Yang*, M. Vamvini*, P. Nigro*, L.-L. Ho, K. Galani, M. Alvarez, Y. Tanigawa, A. Renfro, N. P. Carbone, M. Laakso, L. Z. Agudelo, P. Pajukanta, M. F. Hirshman, R. J.W. Middelbeek, K. Grove, L. Goodyear, M. Kellis, Single-cell dissection of the obesity-exercise axis in adipose-muscle tissues implies a critical role for mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Metab. Cell Metab. 34(10),1578-1593.e6 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.004
Published in Nature, 2023
The consortia released a manuscript describing the results from meta-analysis data freeze version 7.
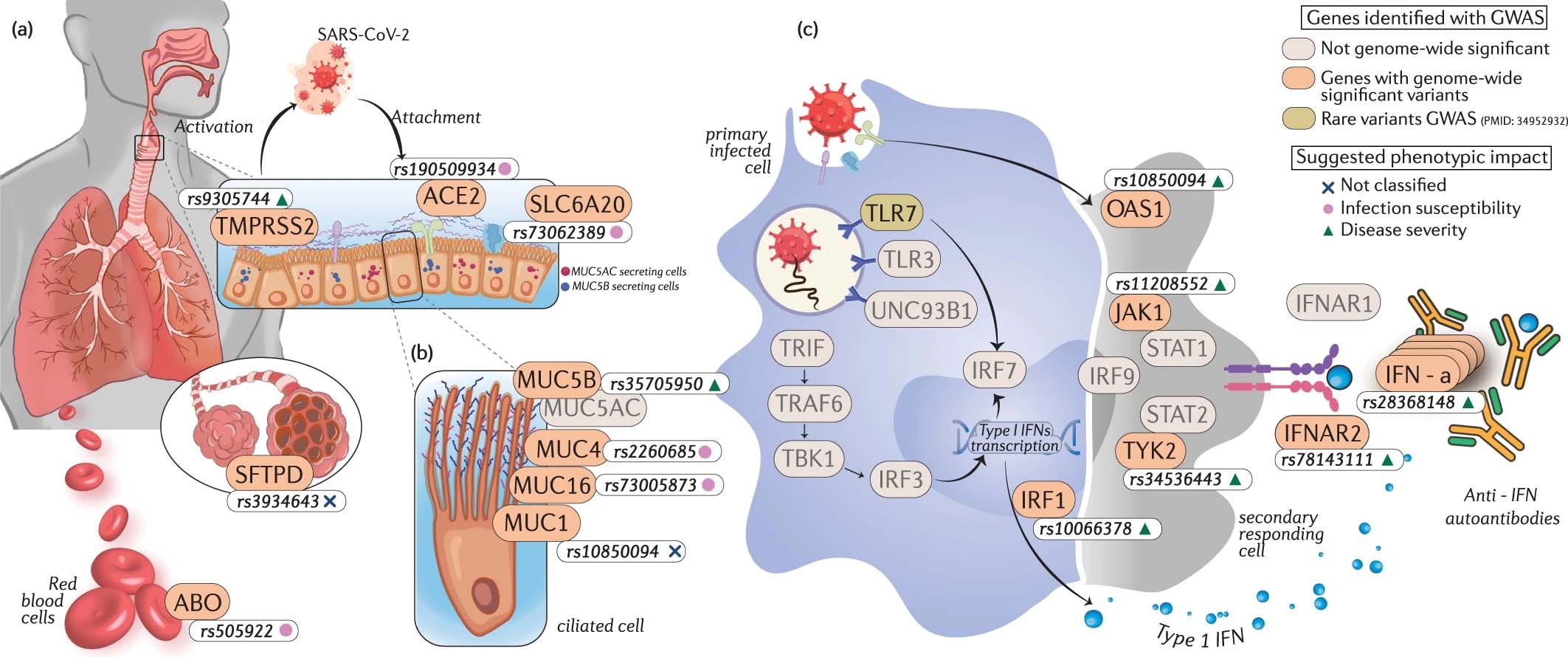
Reference: The COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. A second update on mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. Nature 621(7977), E7-E26 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06355-3
Published in Cell, 2023
Here we report 194,000 single-nucleus microglial transcriptomes and epigenomes across 443 human subjects and diverse Alzheimer’s disease pathological phenotypes.
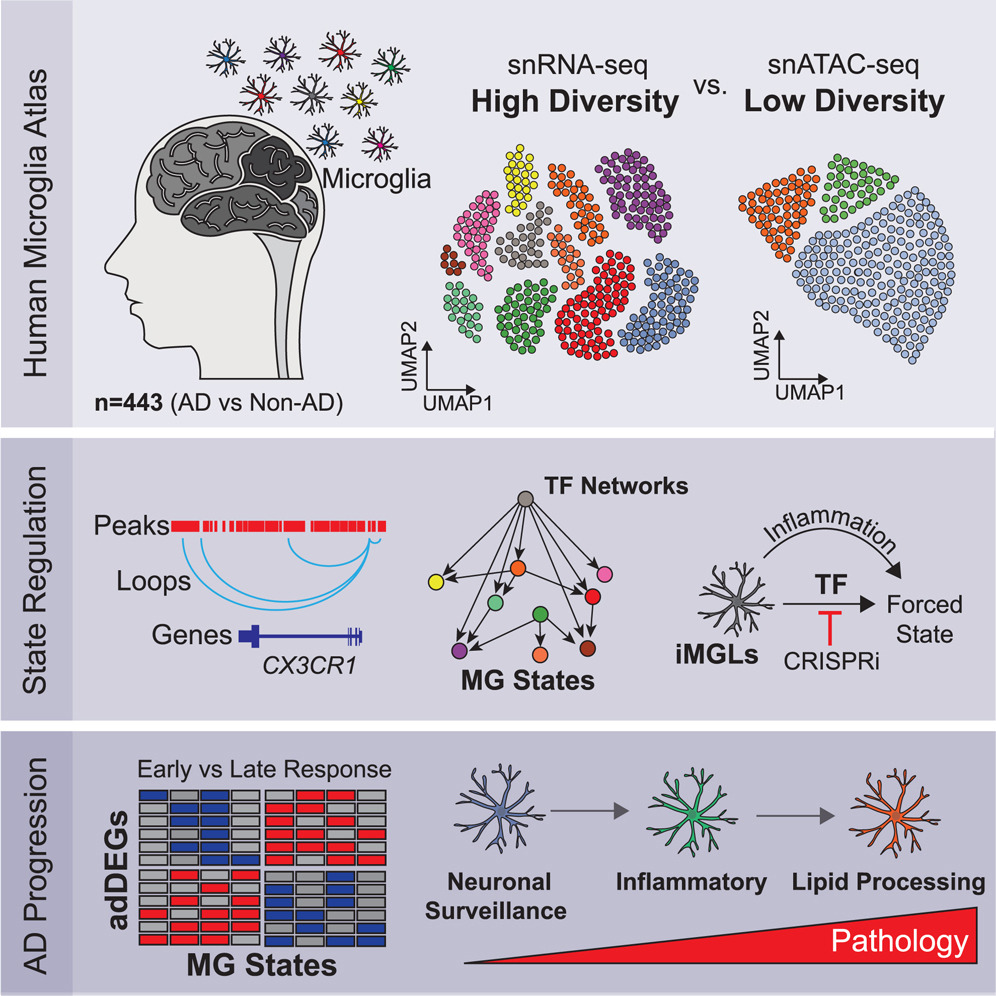
Reference: N. Sun*, M. B. Victor*, Y. P. Park, X. Xiong, A. N. Scannail, N. Leary, S. Prosper, S. Viswanathan, X. Luna, C. A. Boix, B. T. James, Y. Tanigawa, K. Galani, H. Mathys, X. Jiang, A. P. Ng, D. A. Bennett, L.-H. Tsai, M. Kellis. Human microglial state dynamics in Alzheimer's disease progression. Cell 186(20), 4386-4403 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.037
Published in The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2023
We report a new method that improves genetic predictions by directly including admixed and ancestry-diverse individuals. The inclusive training strategy makes genetic prediction models more accurate for everyone, promoting health equity.
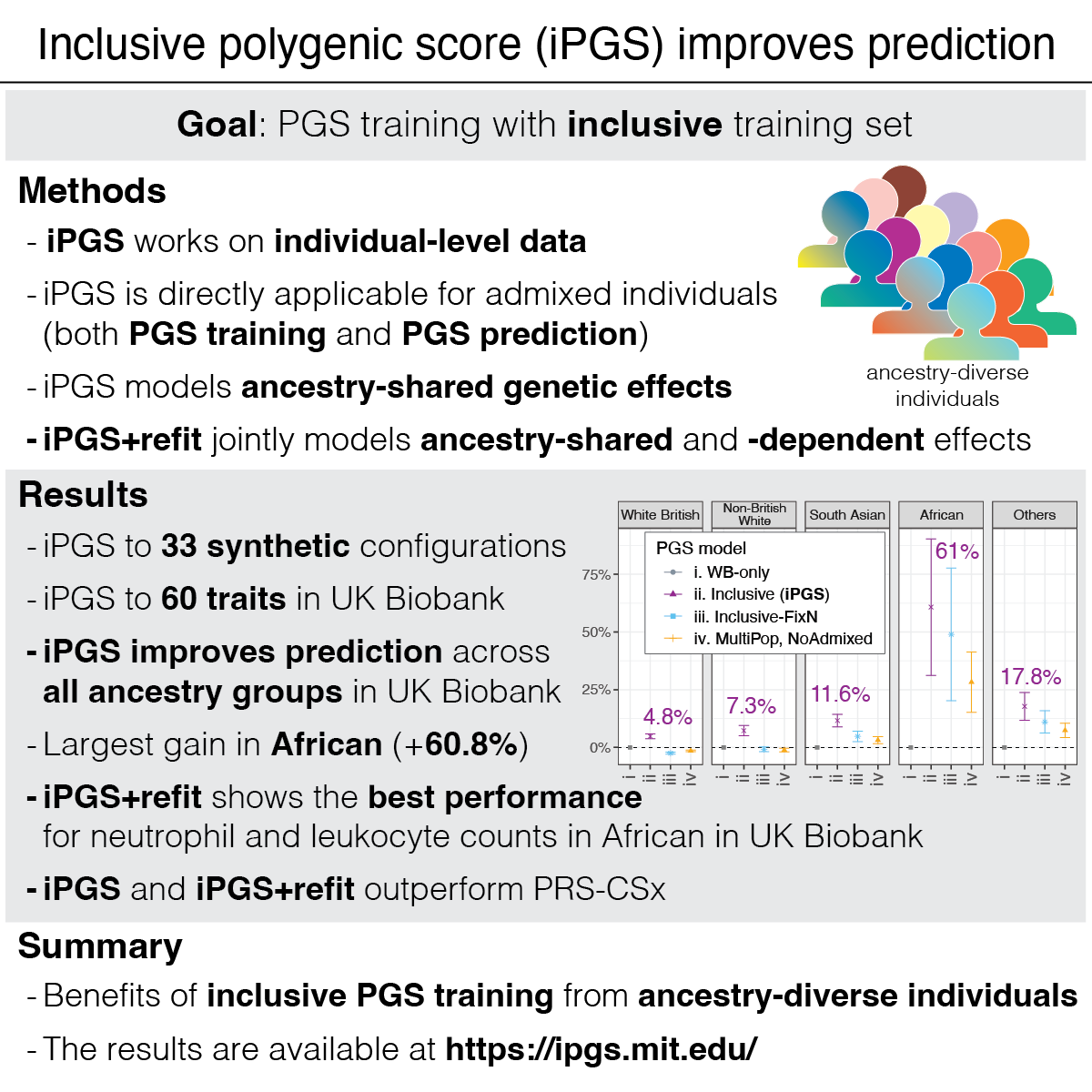
Reference: Tanigawa and Kellis. Power of inclusion: Enhancing polygenic prediction with admixed individuals. The American Journal of Human Genetics. 110, 1888-1902 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.09.013
Published in Nature Communications, 2024
We developed GenoBoost, a polygenic score modeling approach, incorporating both additive and non-additive genetic dominance effects.
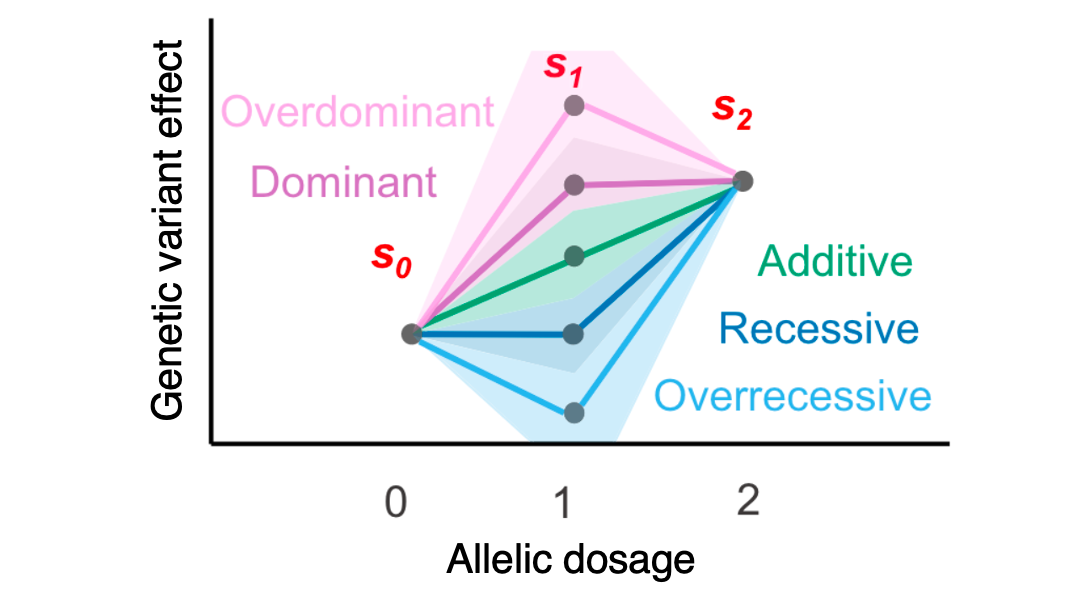
Reference: Ohta*, Tanigawa*, Suzuki, Kellis, and Morishita. A polygenic score method boosted by non-additive models. Nature Communications 15, 4433 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48654-x
Published in The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2024
We introduce “hypometric genetics,” an approach to investigate the genetic basis of binarized traits representing the presence of below-the-limit-of-quantification (BLQ) quality control indicators. We show a joint analysis of BLQ and quantitative traits leads to improved power in genetic discovery, highlighting the value of considering population-based samples and phenotypic extremes in genetic studies
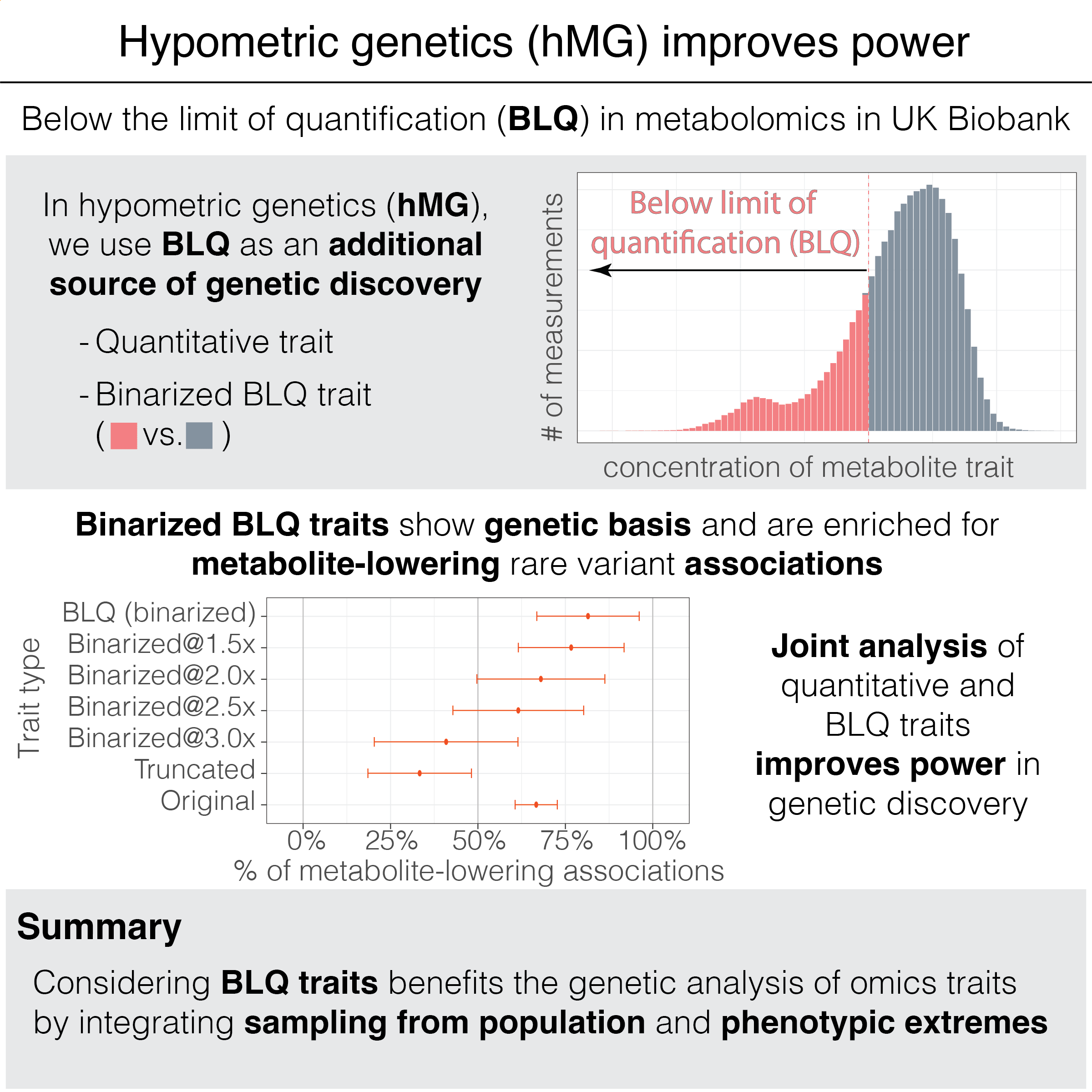
Reference: Tanigawa and Kellis. Hypometric genetics: Improved power in genetic discovery by incorporating quality control flags. The American Journal of Human Genetics. 111(11):2478-2493 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.09.008
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2025
In this study led by Johanne M. Justesen in the Rivas lab, we investigate the genetic basis of cardiometabolic disease progression, ascertained by the time from the initial diagnosis to time to complication/comorbidity diagnosed or procedure in the UK Biobank.
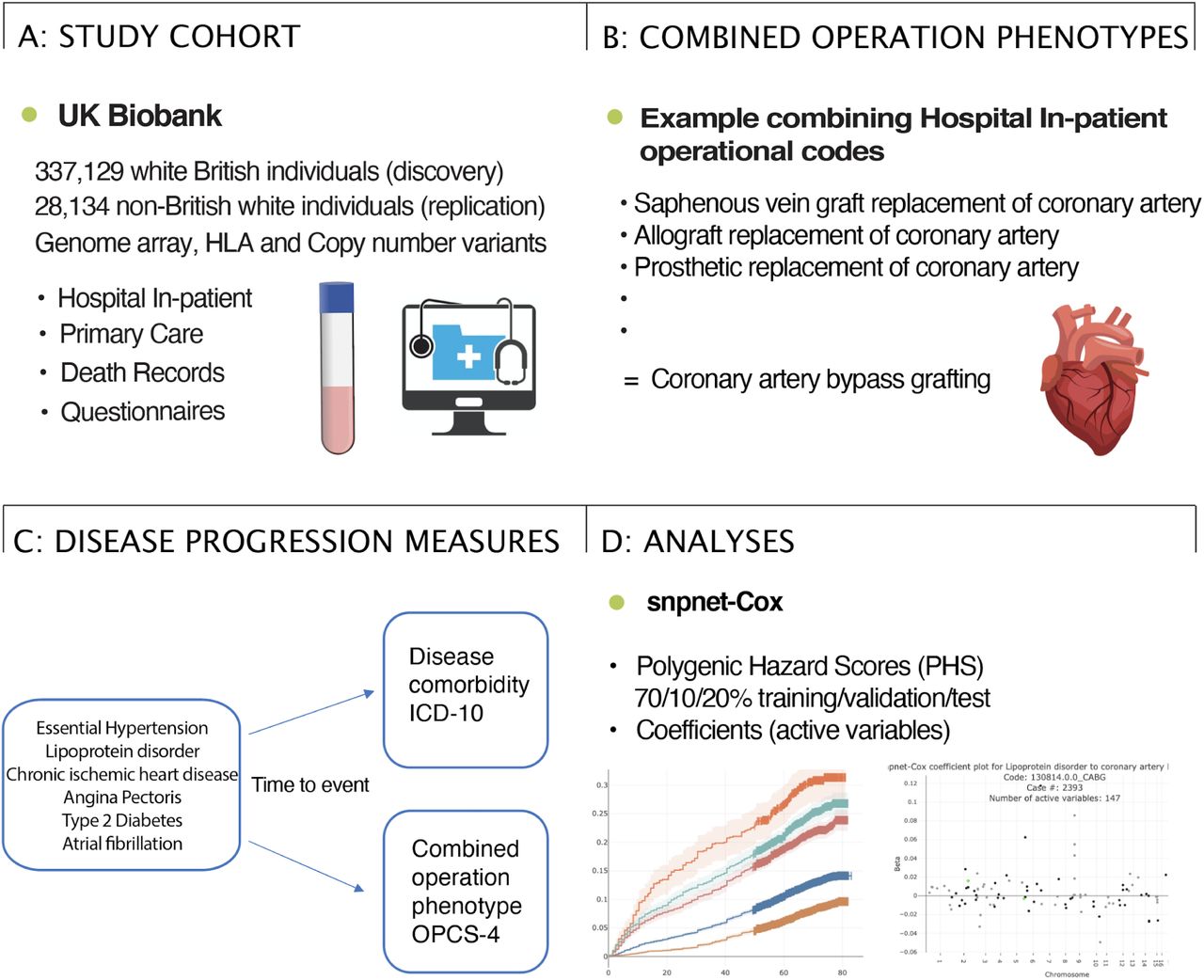
Reference: J. M. Justesen, G. R. Venkataraman, Y. Tanigawa, R. Li, T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, J. W. Knowles, M. A. Rivas, Genetics of cardiometabolic disease progression. medRxiv, 2025.02.01.25321518 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.02.01.25321518
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2025
In this study led by Lei Hou, we report systematic integration of epigenomics data in bipolar disorders.
Reference: Genotype-Epigenome-Phenotype Integration Reveals the Contributions of Peripheral Immune Cells to Bipolar Disorder Pathogenesis, Phenotypic Heterogeneity, and Therapy, J.L. Hou, Y. Li, X. Xiong, Y. Tanigawa, Y. Park, S. W. Lenz, A. Grayson, J.-H. Lee, E. Ryu, J. E. Olson, J. M. Biernacka, M. A. Frye, T. Ordog, M. Kellis. medRxiv, 2025.03.17.25324124 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.03.17.25324124
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2025
In this study jointly led by Matt Victor and Na Sun, we systematically dissect the molecular basis of psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease at single-cell resolution, revealing cellular and regional vulnerabilities associated with psychosis.
Reference: Cellular and Regional Vulnerability Shapes the Molecular Landscape of Psychosis in Alzheimer's Disease, M. B. Victor, N. Sun, K. Galani, N. Leary, Y. Tanigawa, A. N. Scannail, L.-L. Ho, S. Prosper, L. Liu, J. K. Kofler, R. Sweet, L.-H. Tsai, M. Kellis. bioRxiv, 2025.04.30.651435 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.30.651435
Preprint posted on medRxiv, 2025
In this study, led by Hao Zheng, we inferred the demography of presenting authors at major genetic conferences and investigated their longitudinal trends across 26 years.
Reference: Disparities and trends in global representation of human genetics conferences: a 26-year longitudinal study of ASHG and ESHG, H. Zheng, Y. Wang, Y. Tanigawa, J. S. Ong, S. MacGregor, L. Liang, M. Kellis, X. Han. medRxiv, 2025.08.12.25333491 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.08.12.25333491
Published in Cell, 2025
Reference: Z. Liu*, S. Zhang*, B. T. James, K. Galani, R. J. Mangan, S. B. Fass, C. Liang, M. M. Wagle, C. A. Boix, Y. Tanigawa, S. Yun, Y. Sung, X. Xiong, N. Sun, L. Hou, M. Wohlwend, M. Qiu, X. Han, L. Xiong, E. Preka, L. Huang, W. F. Li, L.-L. Ho, A. Grayson, J. Mantero, A. Kozlenkov, H. Mathys, T. Chen, S. Dracheva, D. A. Bennett, L.-H. Tsai, M. Kellis. Single-cell multiregion epigenomic rewiring in Alzheimer’s disease progression and cognitive resilience. Cell 188(18), 4980-5002.e29 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2025.06.031
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2025
In this study, led by Xiaohe (Lucy) Tian, we showed that ancestry-aware integration of tissue-specific genomic annotations enhances the transferability of polygenic scores (PGS).
Reference: PRISM: ancestry-aware integration of tissue-specific genomic annotations enhances the transferability of polygenic scores, X. Tian, T. Fabiha, W. F. Li, K. K. Dey, M. Kellis, Y. Tanigawa. bioRxiv, 2025.11.13.688144 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.11.13.688144
Preprint posted on bioRxiv, 2025
In this work, we introduce sc4D, a spatio-temporal single-cell transcriptomics framework that jointly models cellular state, organization, and disease progression. By integrating autoencoder embeddings with optimal transport, sc4D reconstructs interpretable disease trajectories and predicts in silico perturbation response.
Reference: sc4D: spatio-temporal single-cell transcriptomics analysis through embedded optimal transport identifies joint glial response to Alzheimer's disease pathology. I. Rao, M. Kellis, Y. Tanigawa. bioRxiv, 2025.11.19.689166v1 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.11.19.689166
Published:
We, the Rivas Lab, have aggregated summary statistics from population cohorts, originally from over 330,000 individuals from UK Biobank, and provide a browser and inference engine for the community. As of July 2020, our data now feature over 750,000 individuals across three cohorts: UK Biobank, Million Veterans Program and Biobank Japan.

Resource: Global Biobank Engine https://gbe.stanford.edu/
Published:
We provide an update on Genomic Regions Enrichment of Annotations Tool (version 4) from the Bejerano lab.
Resource: Genomic Regions Enrichment of Annotations Tool (version 4). http://great.stanford.edu/
Published:
As a resource accompanying our recent publication, we provide an interactive web application so that users can test DeGAs (decomposition of genetic associations).
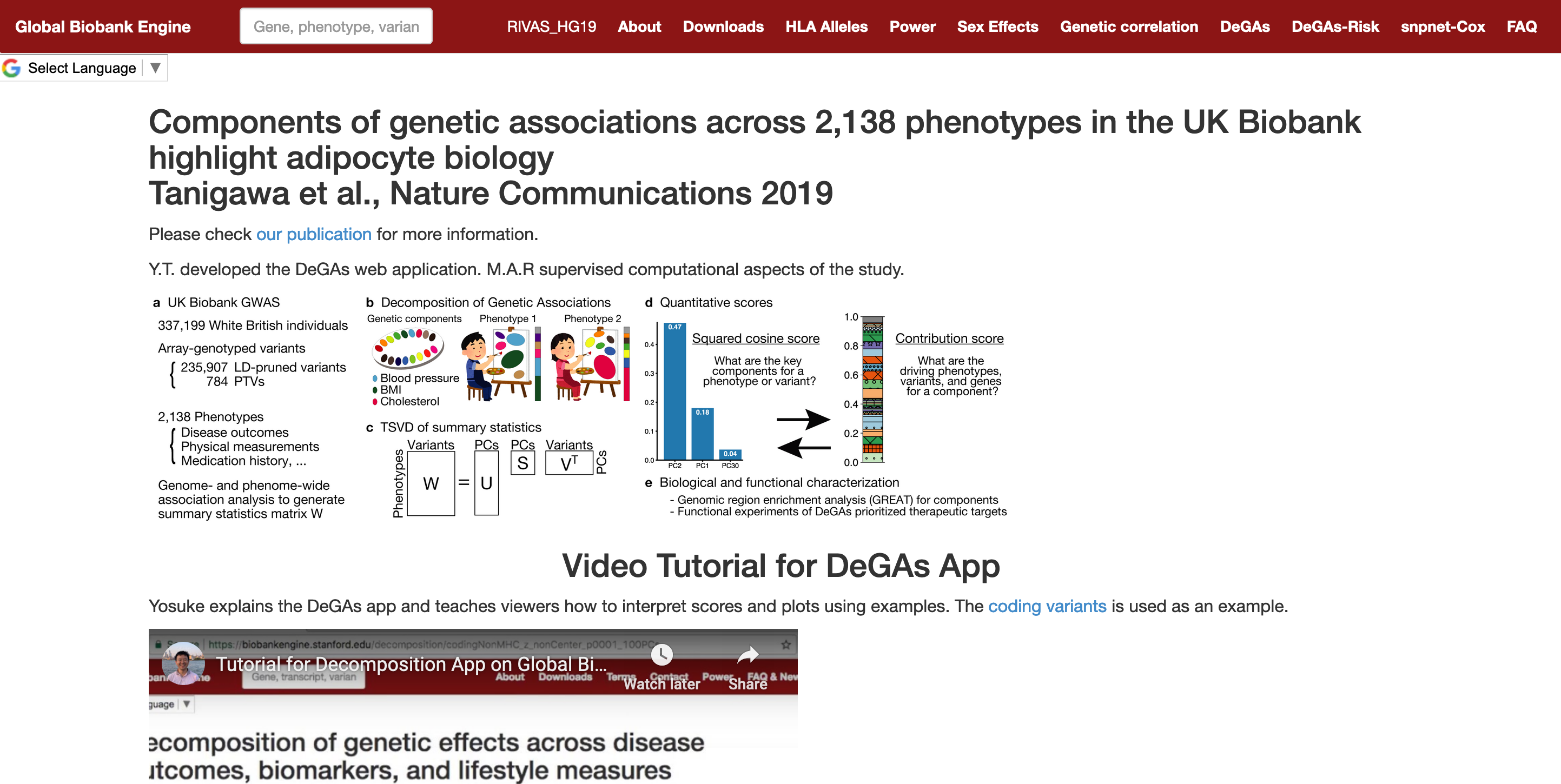
Resource: The DeGAs app in Global Biobank Engine https://gbe.stanford.edu/degas
Published:
We provide datasets described in our DeGAs paper.
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, and M. A. Rivas, Decomposed matrices used for the analysis described in 'Components of genetic associations across 2,138 phenotypes in the UK Biobank highlight adipocyte biology'. (2019). https://doi.org/10.35092/yhjc.9202247.v1
Published:
As a part of the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative, we perform the following set of analyses to better understand the genetic basis of COVID-19 susceptibility and severity.
Resource: The Rivas Lab's COVID-19 Host Genetics analysis repository https://github.com/rivas-lab/covid19
Published:
We provide datasets described in our ANGPTL7 paper.

Reference: Y. Tanigawa, and M. A. Rivas, Datasets described in 'Rare protein-altering variants in ANGPTL7 lower intraocular pressure and protect against glaucoma'. National Institutes of Health. Collection. (2020) https://doi.org/10.35092/yhjc.c.4990529.v1
Published:
We provide datasets described in our biomarker manuscript.

Reference: Y. Tanigawa, N. Sinnott-Armstrong, C. Benner, and M. A. Rivas, Datasets described in 'Genetics of 35 blood and urine biomarkers in the UK Biobank'. National Institutes of Health. Collection. (2020). https://doi.org/10.35092/yhjc.c.5043872.v1
Published:
We provide analysis and visualization scripts used in our biomarker manuscript from the Rivas lab.

Resource: The analysis and visualization scripts used in our biomarker manuscript from the Rivas lab https://github.com/rivas-lab/biomarkers
Published:
We provide the polygenic risk score models computed for Testosterone described in the sex-specific genetic effects on biomarker manuscript.
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, E. Flynn, and M. A. Rivas, The snpnet polygenic risk score coefficients for Testosterone levels described in 'Sex-specific genetic effects across biomarkers'. figshare. Dataset. (2020). https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12793490.v1
Published:
I was one of the invited guest speakers at Statistical genetics summer school at Osaka University.

Published:
I gave a research-in-progress talk in our department seminar.
Published:
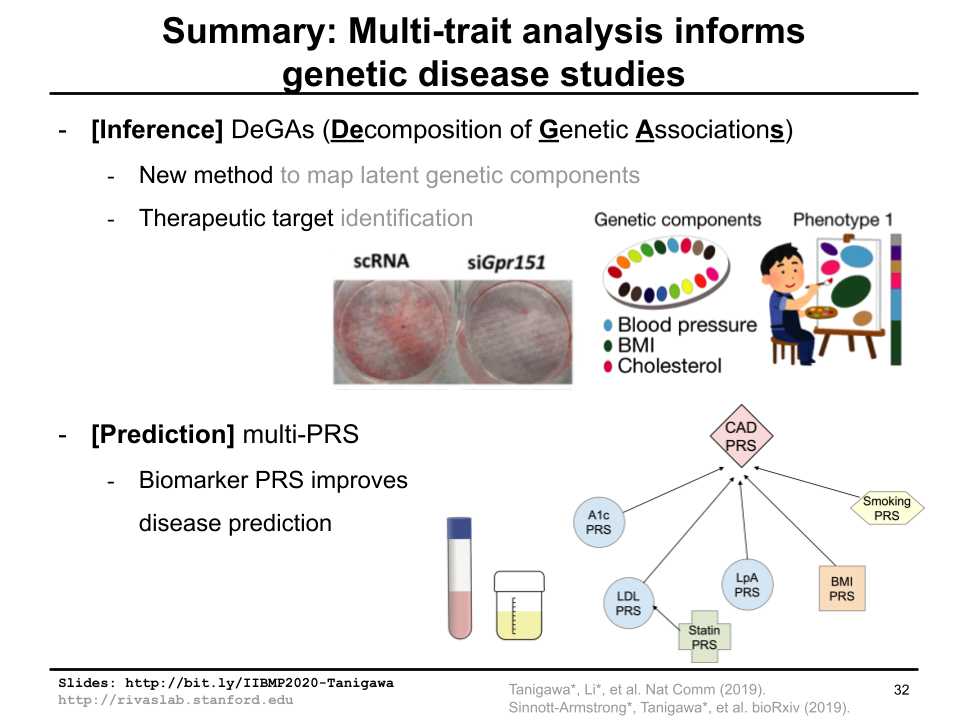
I had a wonderful opportunity to give a virtual oral presentation at Informatics in Biology, Medicine, and Pharmacology conference, 2020. I talked about joint analysis of multiple traits in genetic disease studies using DeGAs and multi-PRS as example projects.
Published:
I had a fantastic opportunity to present a poster on WhichTF at the 13th annual RECOMB/ISCB Conference on Regulatory & Systems Genomics with DREAM Challenges.
Reference: Y. Tanigawa, E. Dyer, and G. Bejerano. WhichTF is functionally important in your open chromatin data? [version 1; not peer reviewed]. F1000Research 2021, 10(ISCB Comm J):252 (slides) https://doi.org/10.7490/f1000research.1118533.1
Published:
I presented and successfully defended my thesis titled “Large-scale genomic inference of multiple phenotypes.” Thank you very much for everyone who supported me along the way.
Published:
I was invited to give a presentation at Journal Club meeting at Debora Marks’s lab
Published:
I presented on our recent works on polygenic score analyses across multiple phenotypes at University of Osaka.
Published:
Published:
At GREGoR Consortium Stanford Sitewide Meeting, I presented our recent work on ranking transcription factors using ontology-guided stratified enrichment of conserved TFBSs in open chromatin regions.
Published:
Published:
Yosuke presented his recent works on inclusive polygenic score (iPGS) and multi-PRS at University of Bonn.

Published:
Yosuke presented his recent works on inclusive polygenic score (iPGS) at German Biometric and Biostatistics Conference.
Published:
Yosuke presented his recent works on inclusive polygenic score (iPGS) at Biosoc seminar at Princeton University.
Published:
Yosuke presented his recent works on inclusive polygenic score (iPGS) at RECOMB 2024 and RECOMB-Genetics 2024.
Published:
Yosuke presented his recent works on inclusive polygenic score (iPGS) at ASA STATGEN 2024.
Published:
Yosuke presented his research overview at UJA.
Published:
Yosuke presented his research overview at Boston Japanese Researchers Forum.
Published:
Yosuke presented his research at Department of Computational Biology and Medical Sciences, UTokyo.
Published:
Yosuke presented his recent works on inclusive polygenic score (iPGS) at Southern California Symposium on Polygenic Risk Scores.
Published:
Published:
Welcome to UCLA Bioengineering! I am excited to share our research on disease heterogeneity dissection.
Published:
I am excited to attend the ASHG 2025 Annual Meeting. I am looking forward to learn the latest in human genetics research, presenting our work, and meeting (old & new) friends. The Tanigawa Lab is recruiting; please find me for a coffee.
Published:
I am excited to present our recent and ongoing efforts on polygenic score modeling at UCLA’s Frontiers in Bioinformatics seminar.

Published:
I’m excited to present on our recent work on incorporating genomic annotations in polygenic scores at Germany’s online symposium on Recent Advances in Polygenic Score Modeling.
Graduate course, Stanford University, Department of Biomedical Data Science, 2018
I was a teaching assistant for a graduate-level class, BIODS215: Topics in Biomedical Data Science, Large-scale inference. I taught a section on “Data visualization”, hosted office hours, maintained the class website, and graded the assignments.
Graduate course, Stanford University, Department of Biomedical Data Science, 2019
I was a teaching assistant for a graduate-level class, BIOMEDIN 210: Modeling Biomedical Systems: Ontology, Terminology, Problem Solving (CS 270).
Graduate course, Stanford University, Department of Biomedical Data Science, 2020
I was a teaching assistant for a graduate-level class, BIODS215: Topics in Biomedical Data Science, Large-scale inference. I taught a section on “Reproducible large-scale inference”, hosted office hours, maintained the class website, and graded the assignments.
Undergraduate course, Stanford University, 2021
I have been fortunate to give a guest lecture for “Japanese Companies and Japanese Society” (ENGR159Q) taughed by Prof. Robert Sinclair during my time at Stanford.